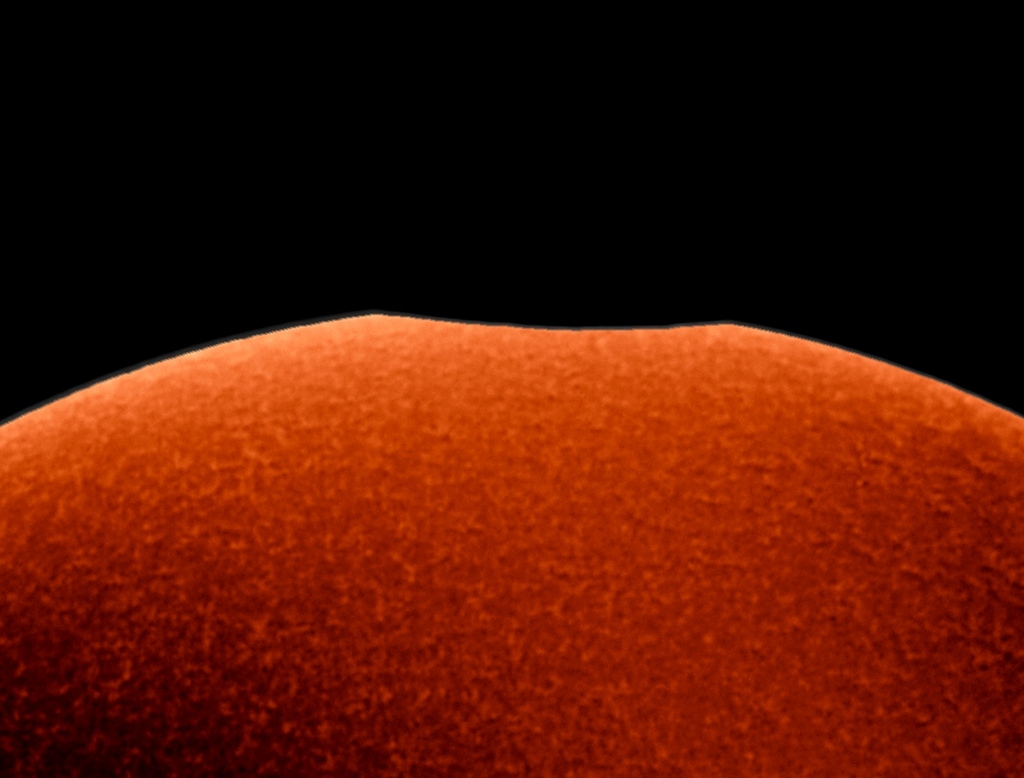
The smallest of the three partial solar eclipses during 2018 was just yesterday, Friday, July 13. It was mostly visible over the open ocean between Australia and Antarctica. Still, this video frame of a tiny nibble on the Sun was captured through a hydrogen-alpha filter from Port Elliott, South Australia, during the maximum eclipse visible from that location. There, the New Moon covered about 0.16 percent of the solar disk. The greatest eclipse, about one-third of the Sun's diameter blocked by the New Moon, could be seen from East Antarctica near Peterson Bank, where the local emperor penguin colony likely had the best view. During this prolific eclipse season, the coming Full Moon will bring a total lunar eclipse on July 27, followed by yet another partial solar eclipse at the next New Moon on August 11. via NASA https://ift.tt/2Liqnhg