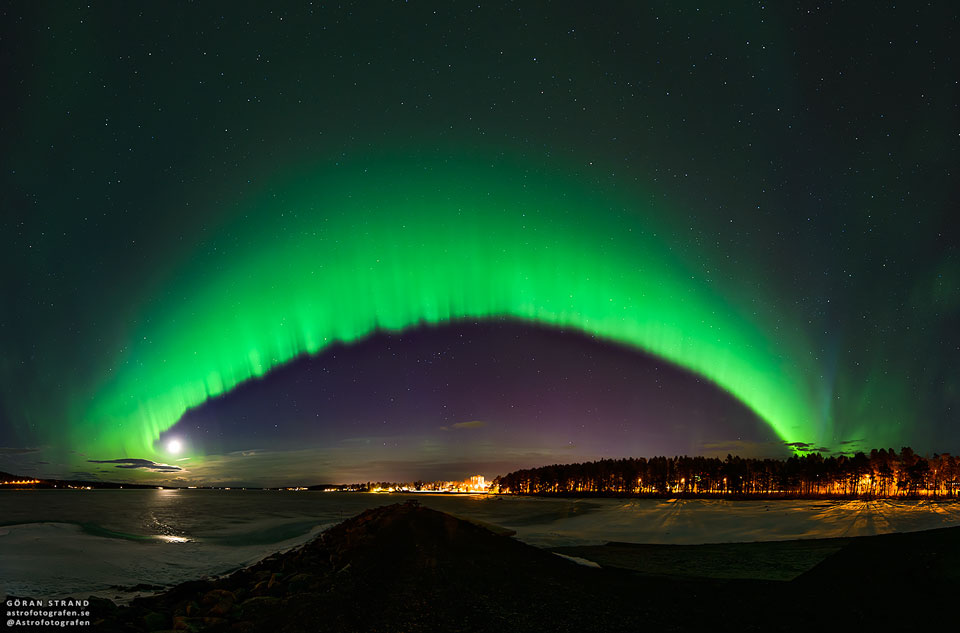
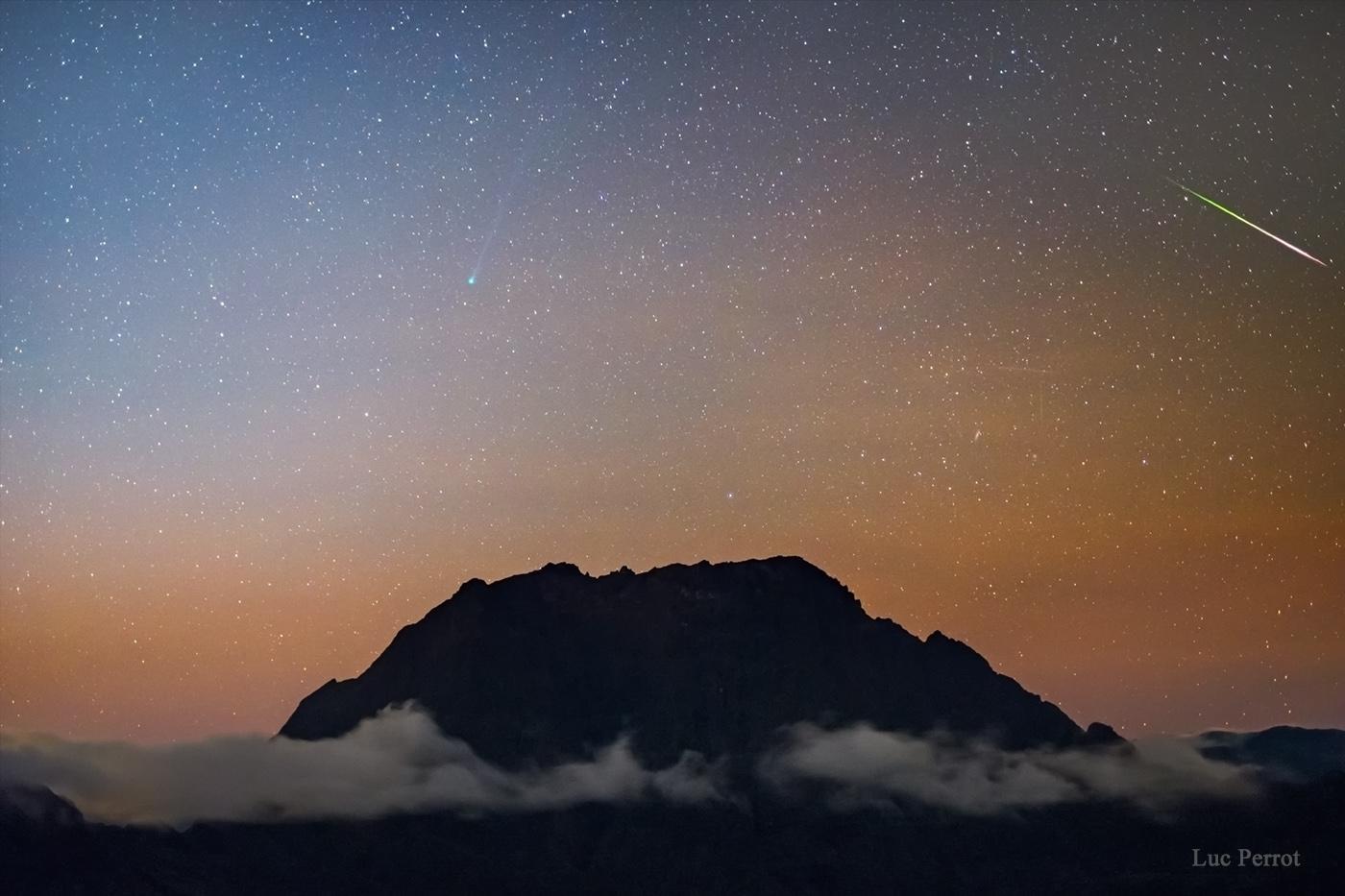
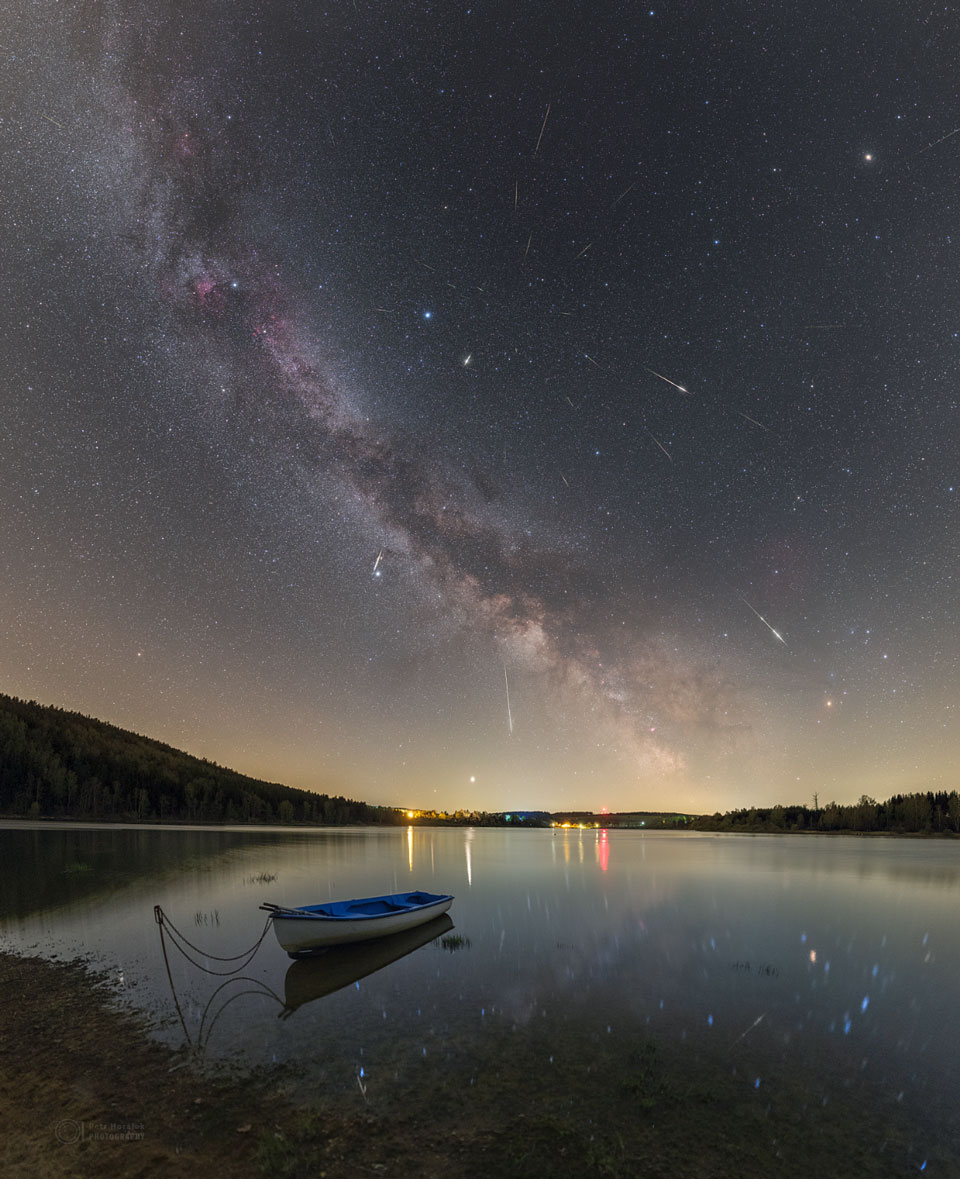
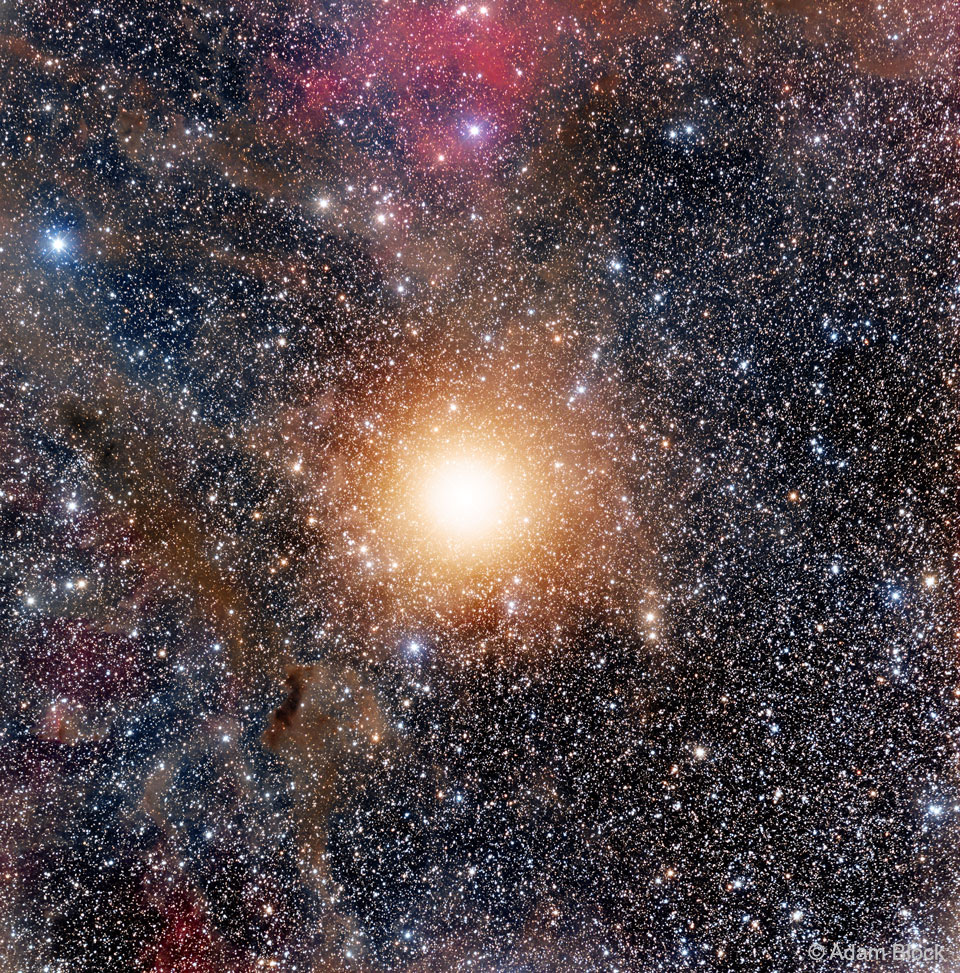
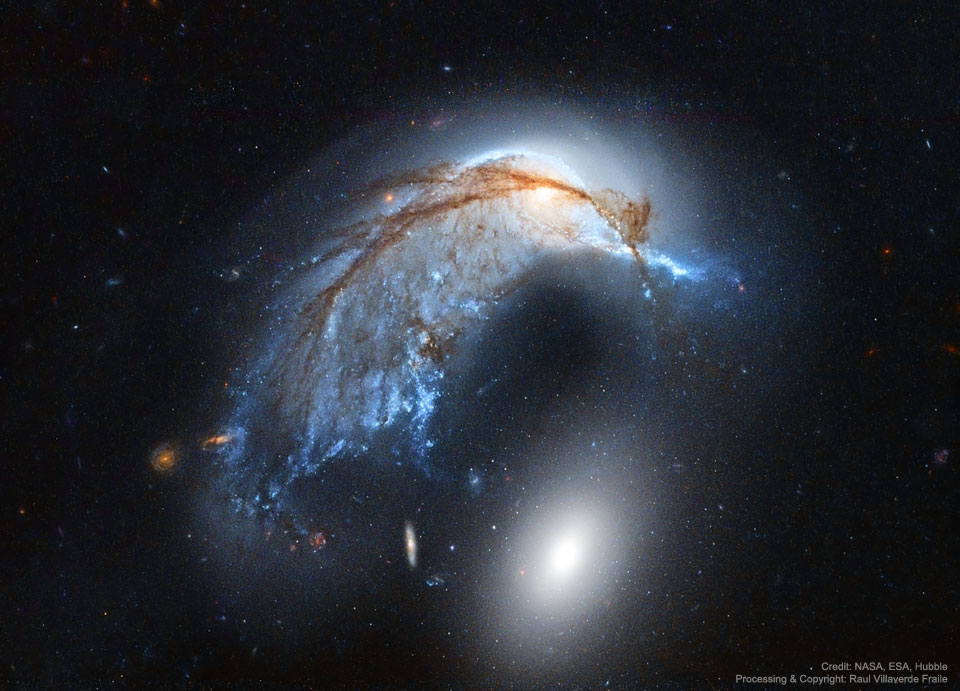
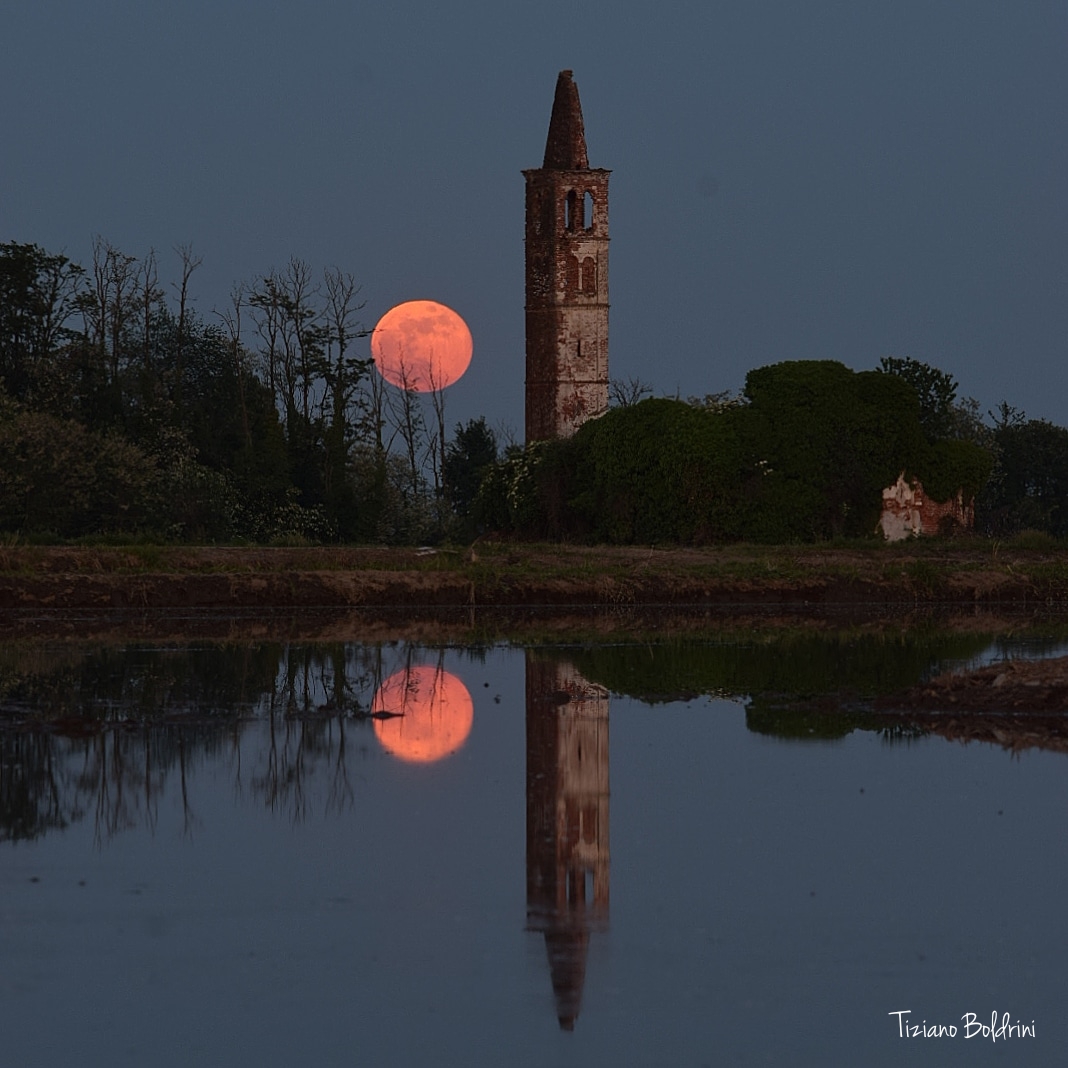
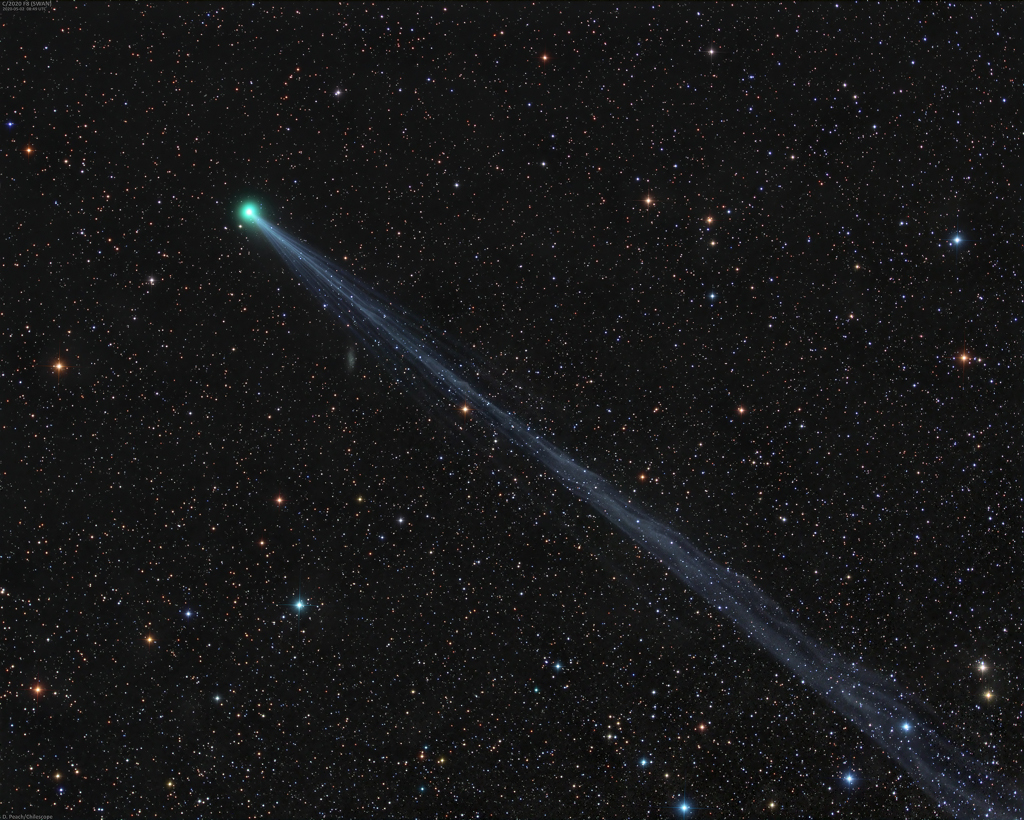
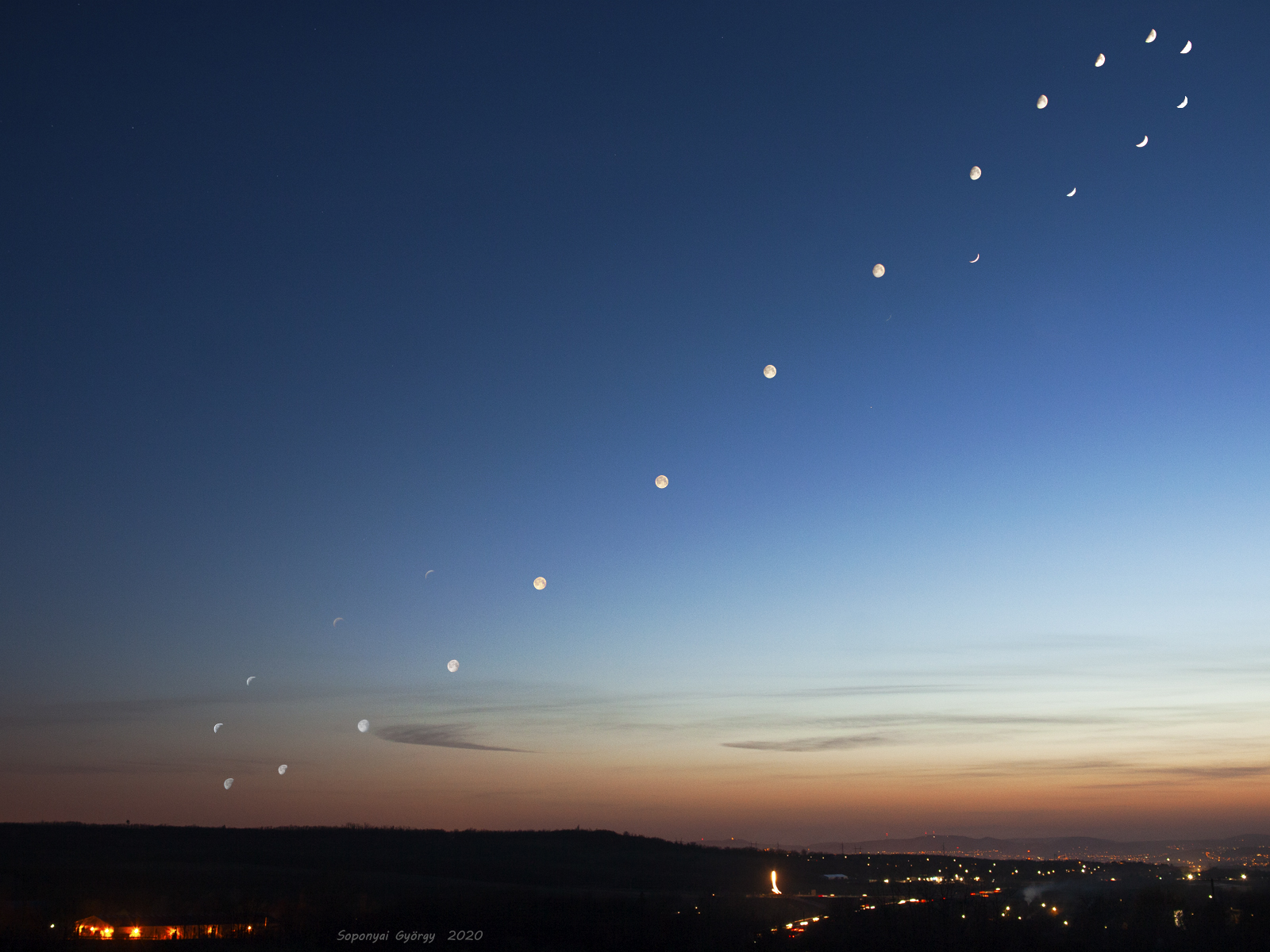
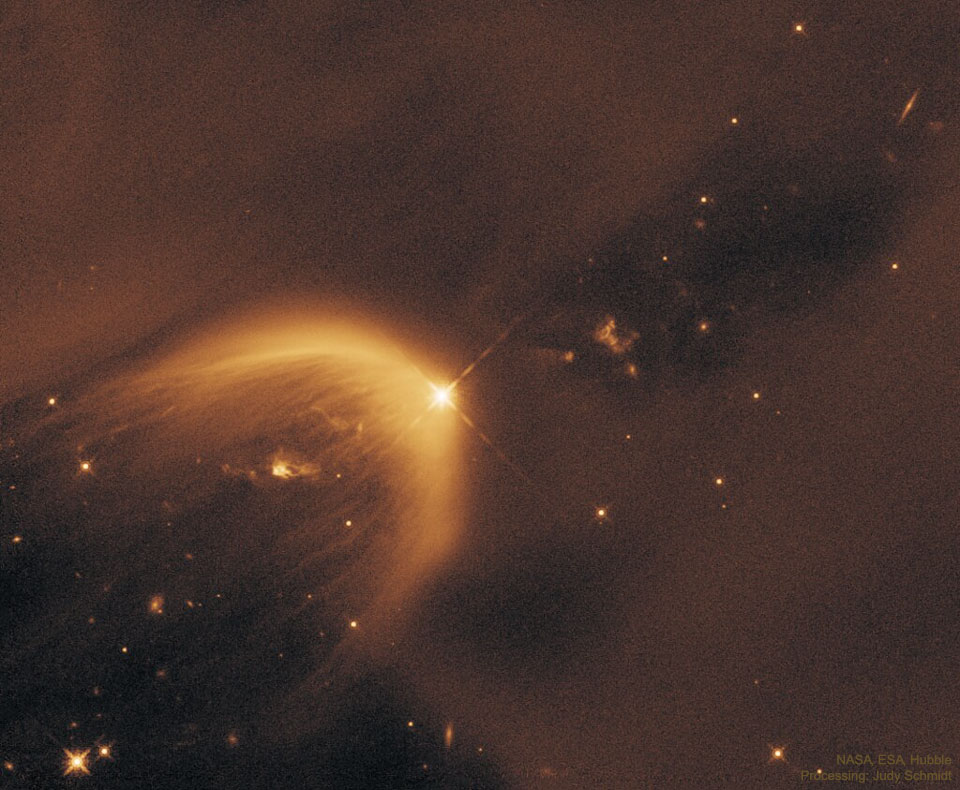
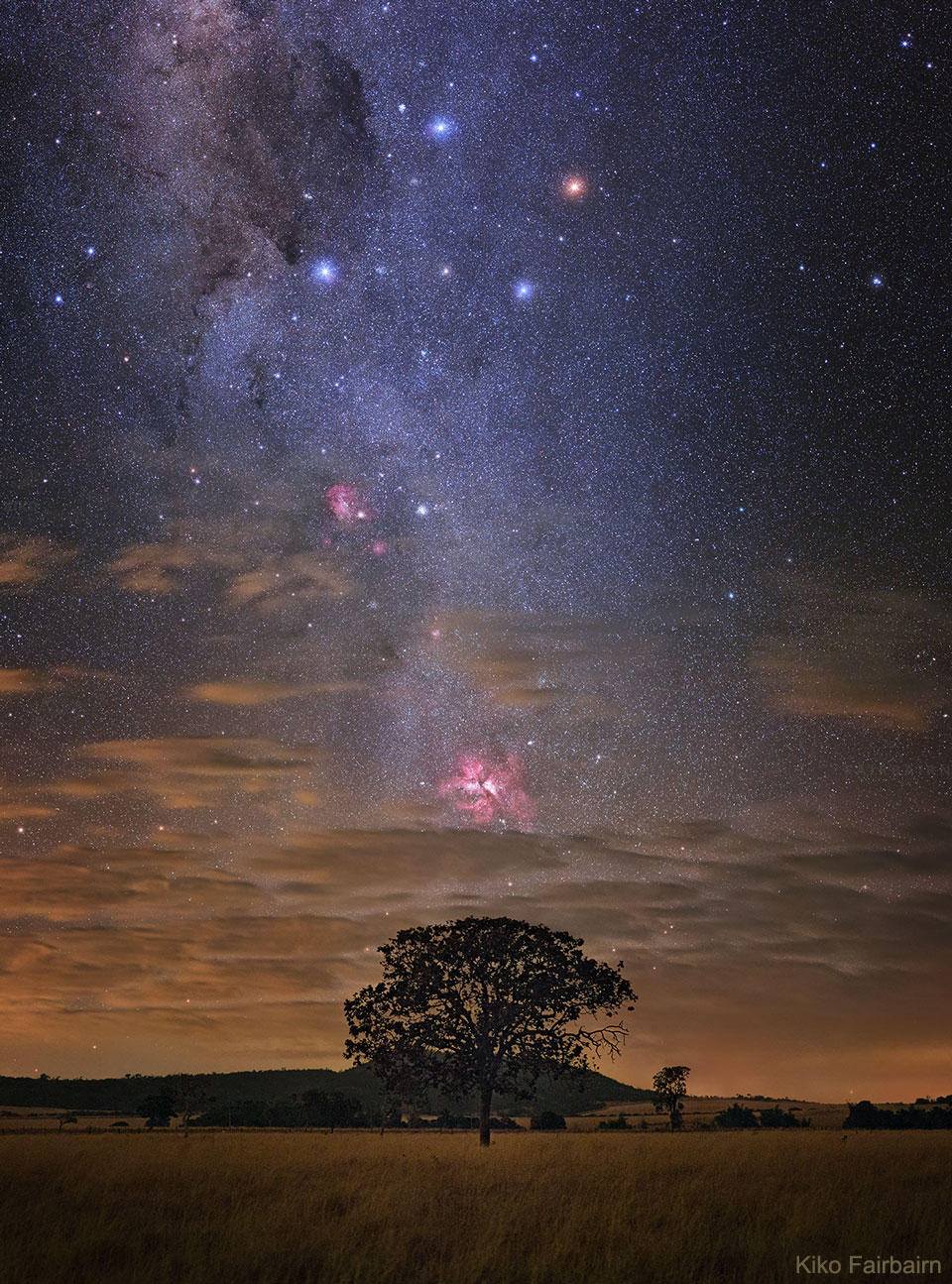
It was bright and green and stretched across the sky. This striking aurora display was captured in 2016 just outside of Östersund, Sweden. Six photographic fields were merged to create the featured panorama spanning almost 180 degrees. Particularly striking aspects of this aurora include its sweeping arc-like shape and its stark definition. Lake Storsjön is seen in the foreground, while several familiar constellations and the star Polaris are visible through the aurora, far in the background. Coincidently, the aurora appears to avoid the Moon visible on the lower left. The aurora appeared a day after a large hole opened in the Sun's corona allowing particularly energetic particles to flow out into the Solar System. The green color of the aurora is caused by oxygen atoms recombining with ambient electrons high in the Earth's atmosphere. via NASA https://ift.tt/2TTTA8t