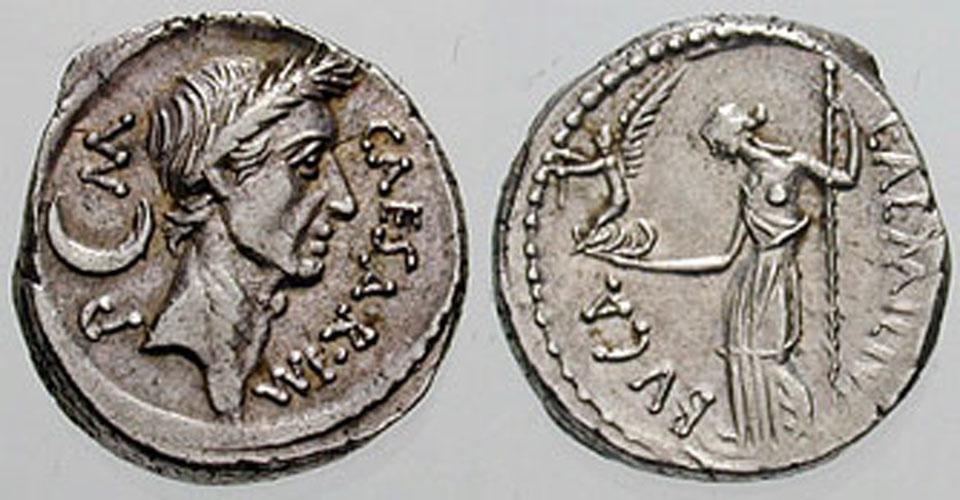
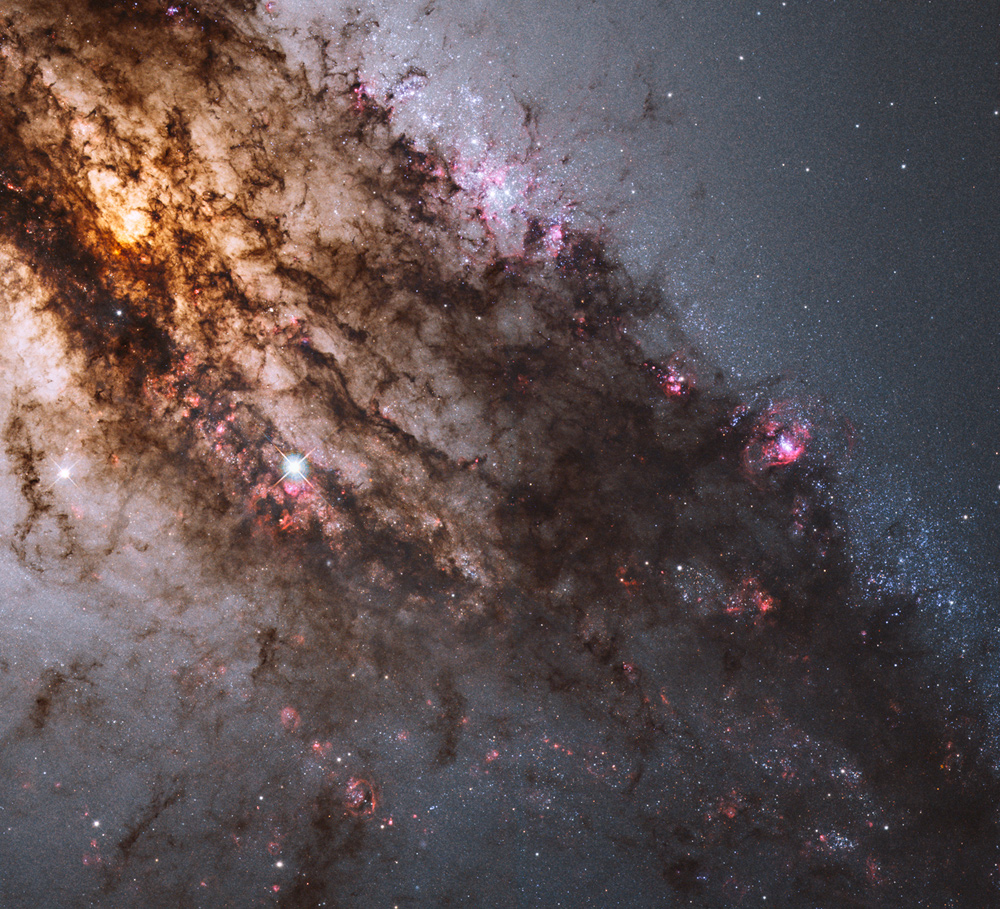
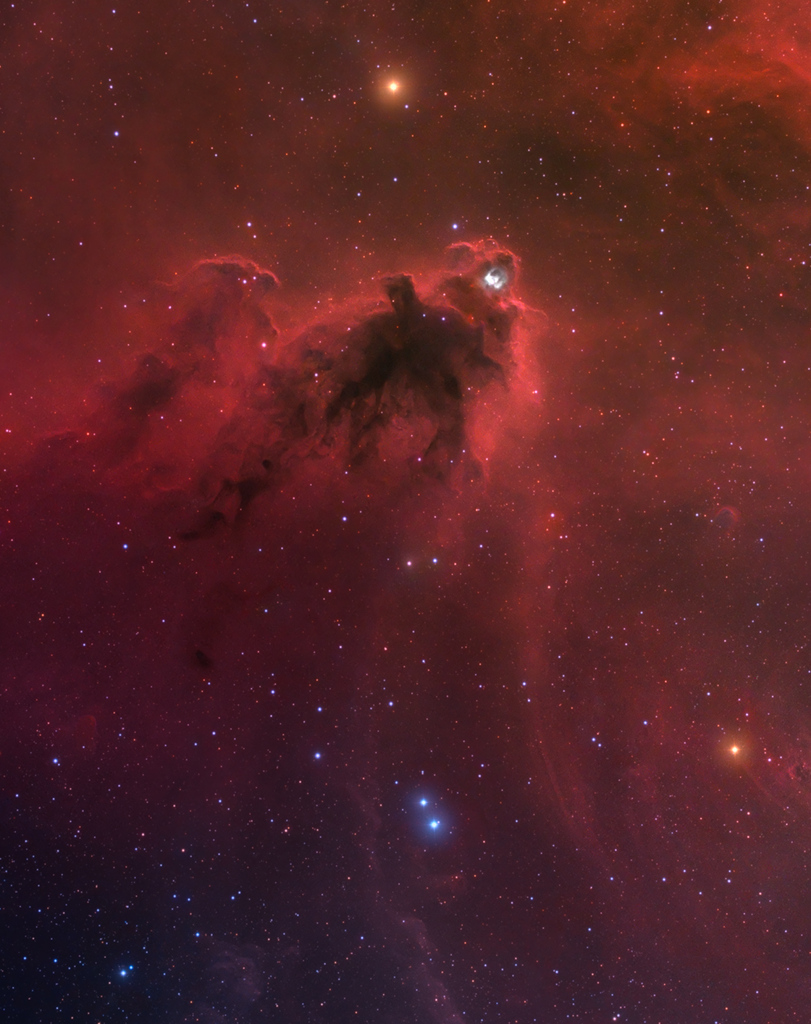
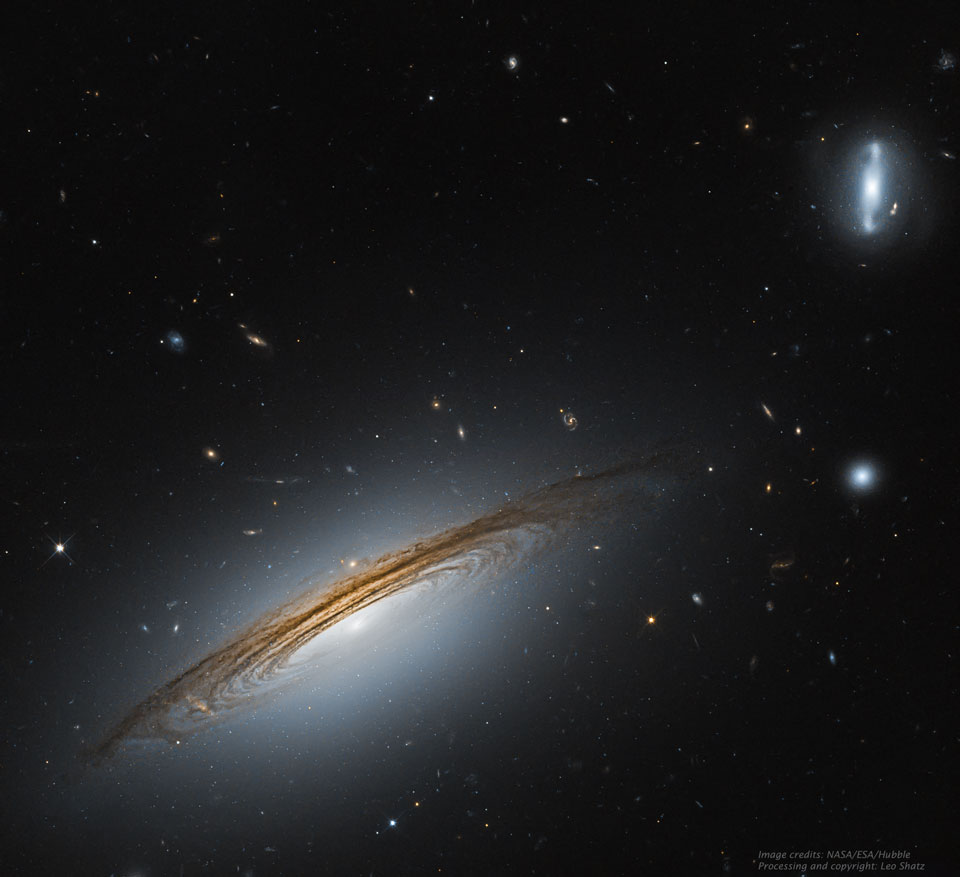
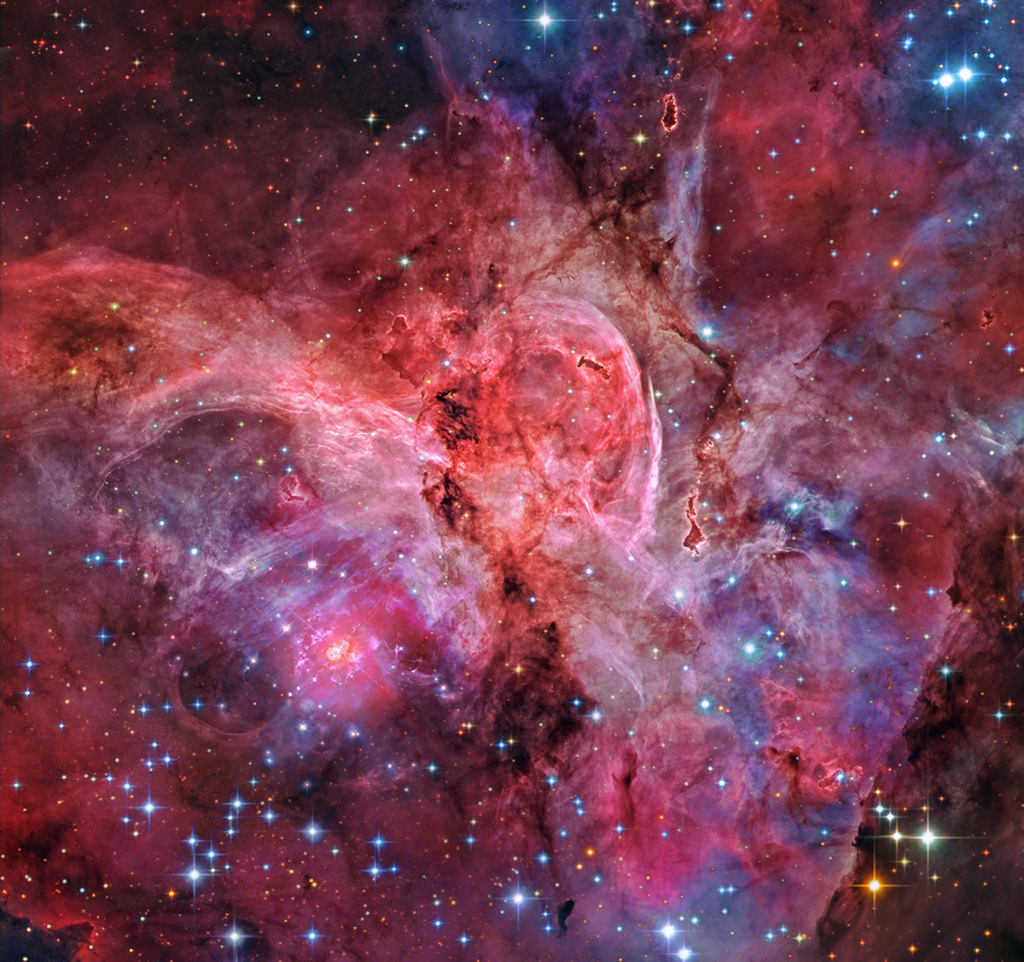
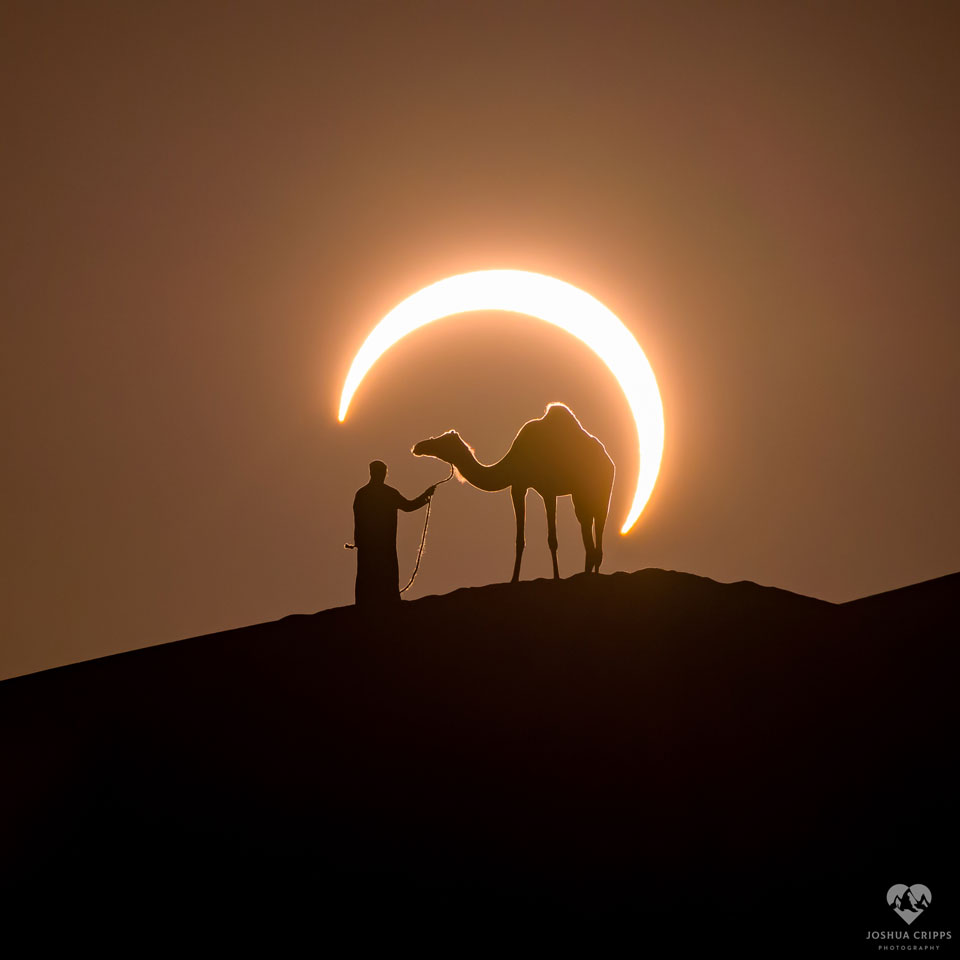
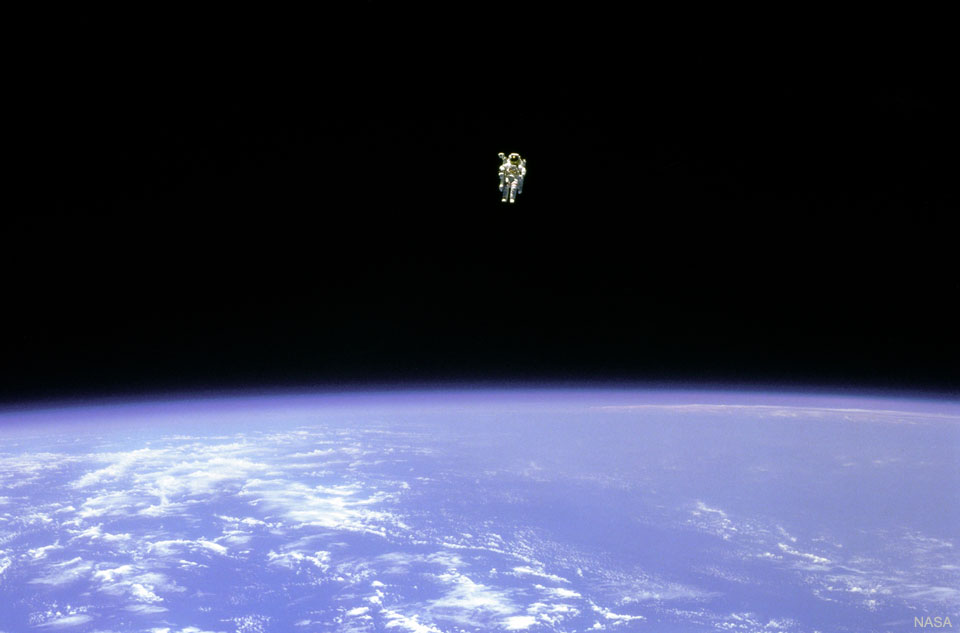
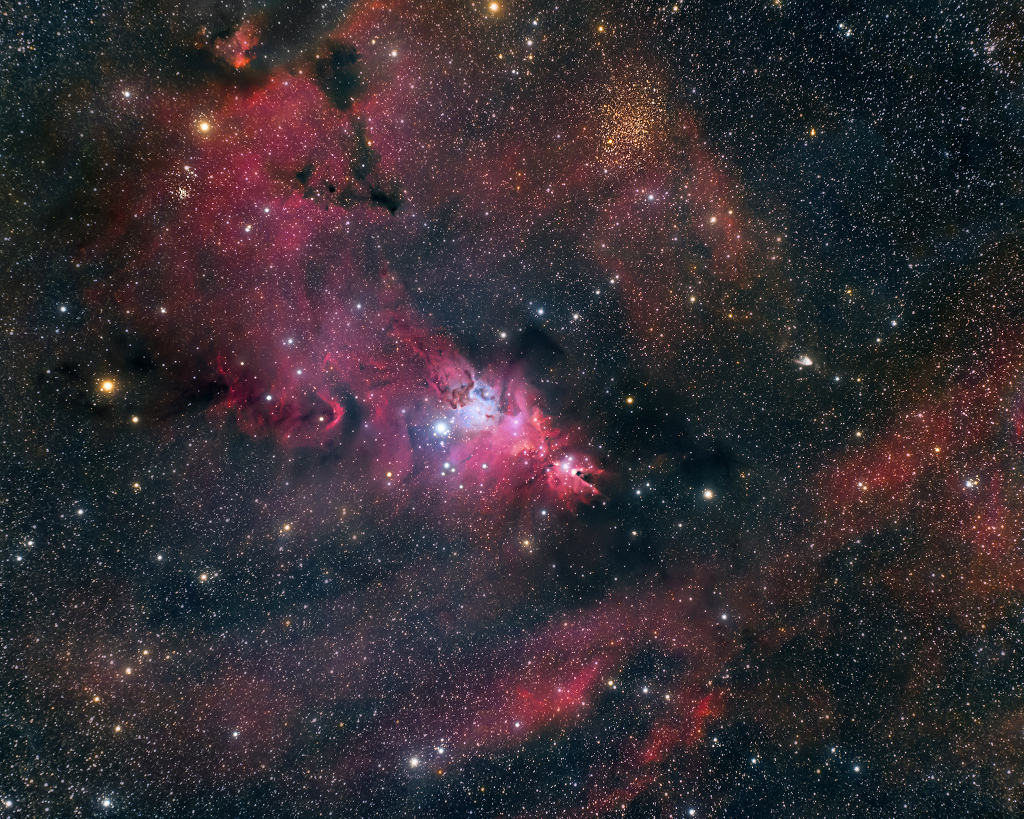
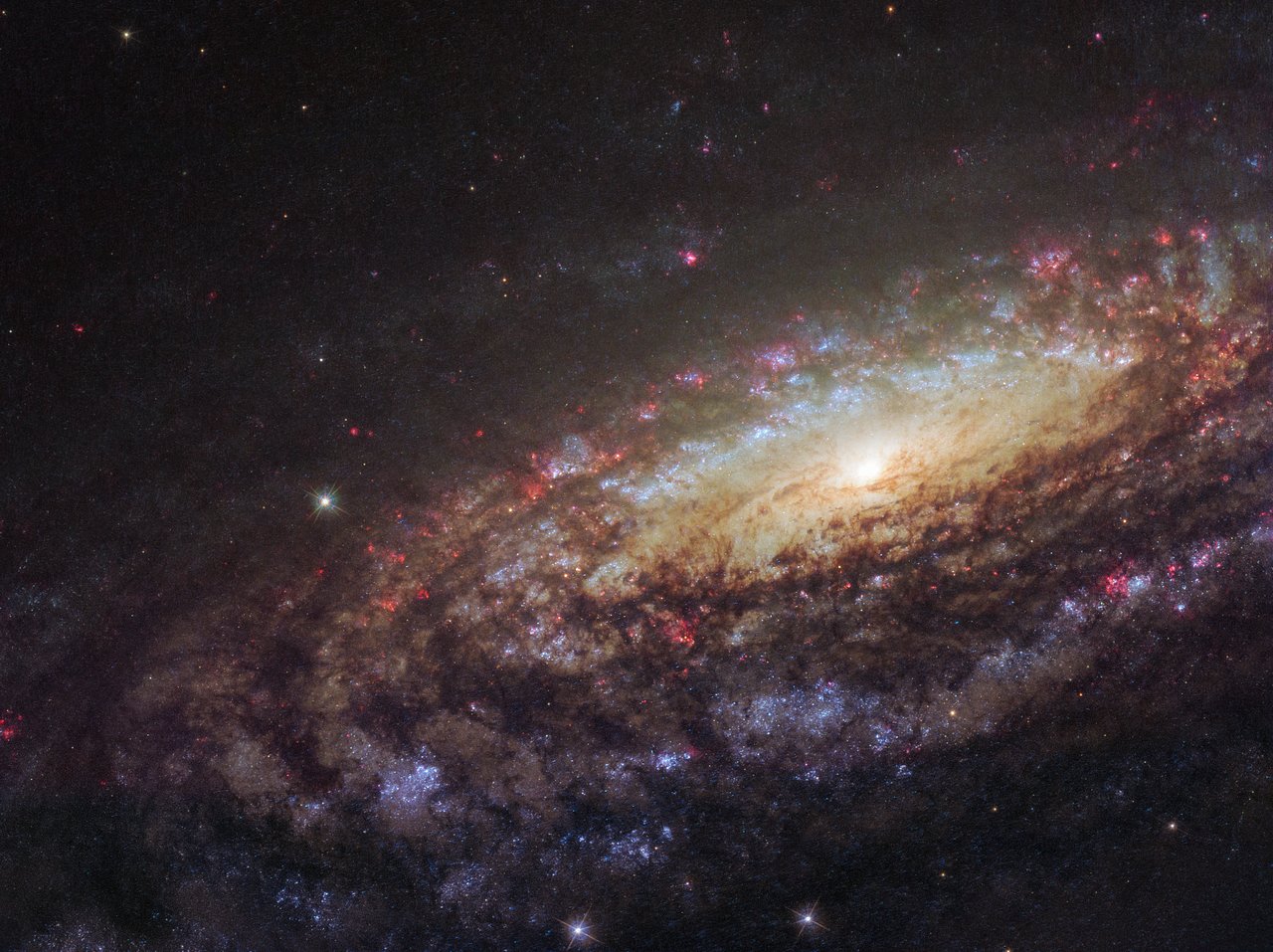
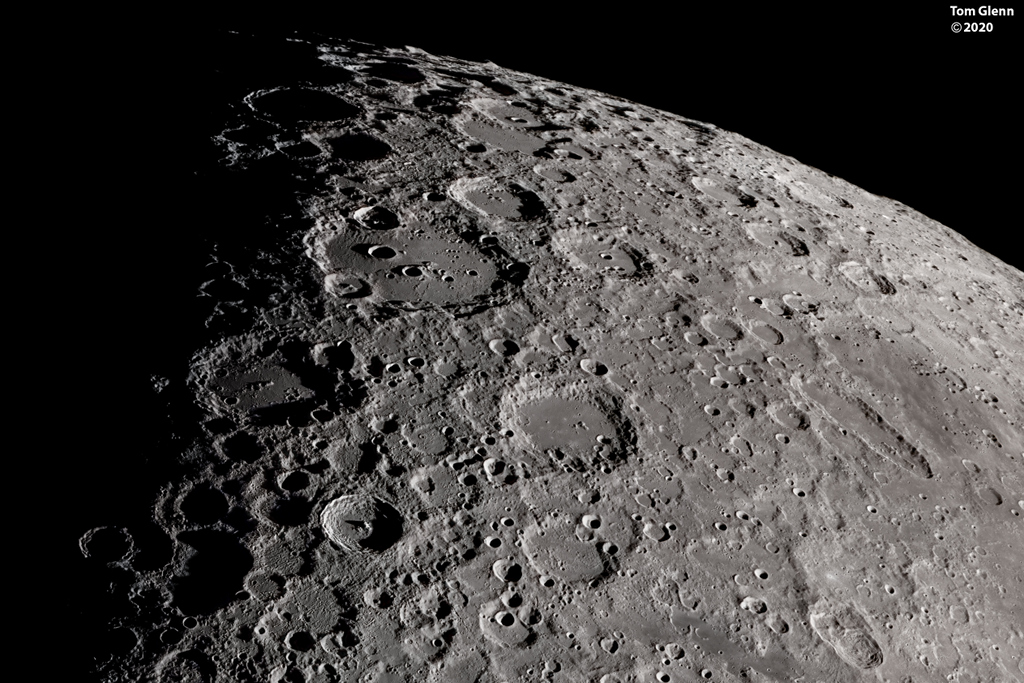
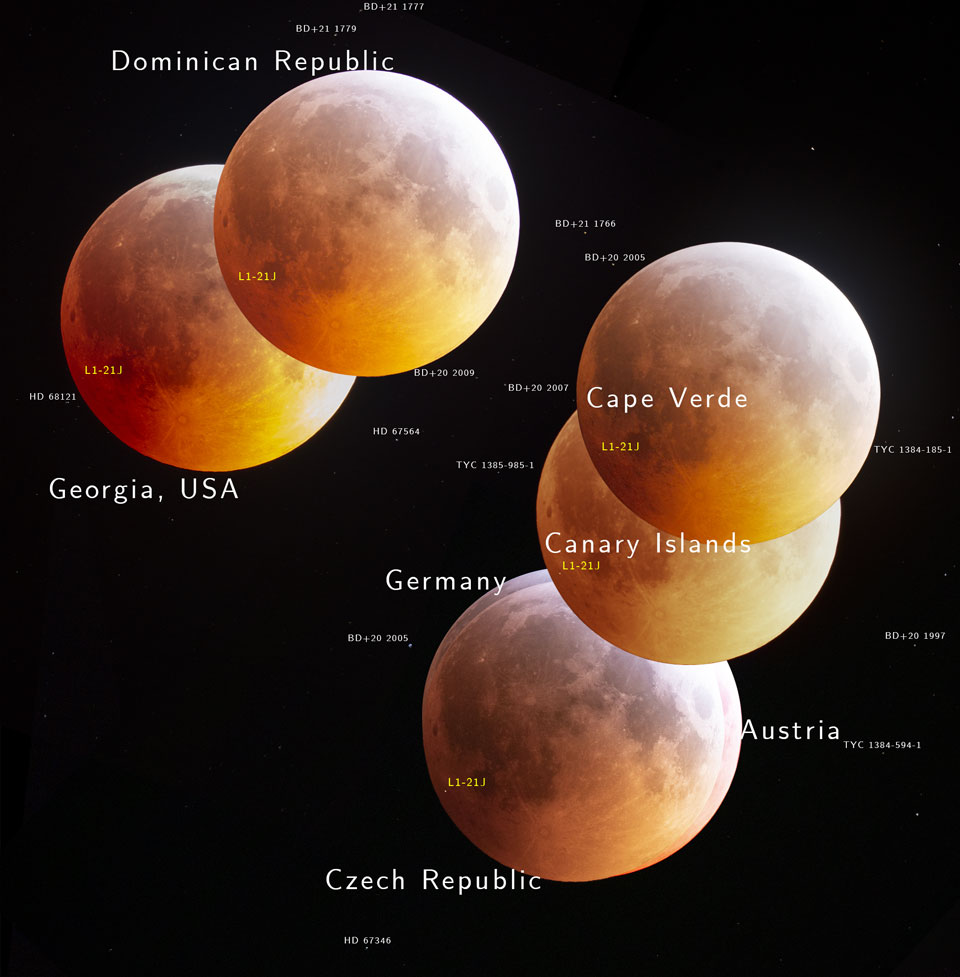
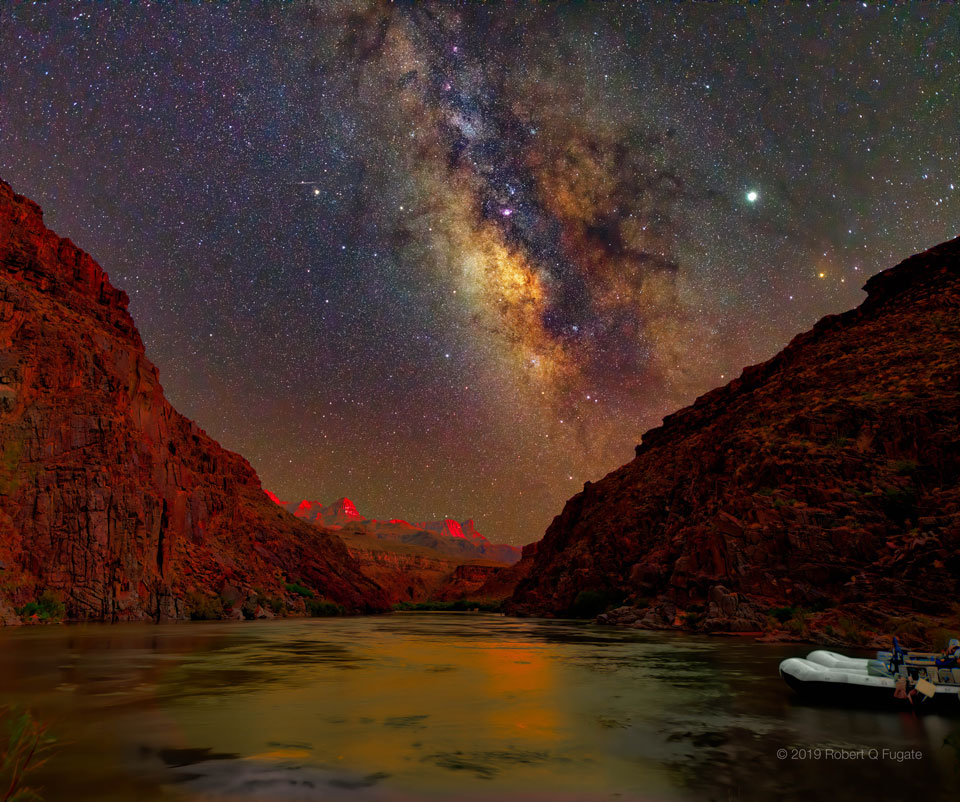
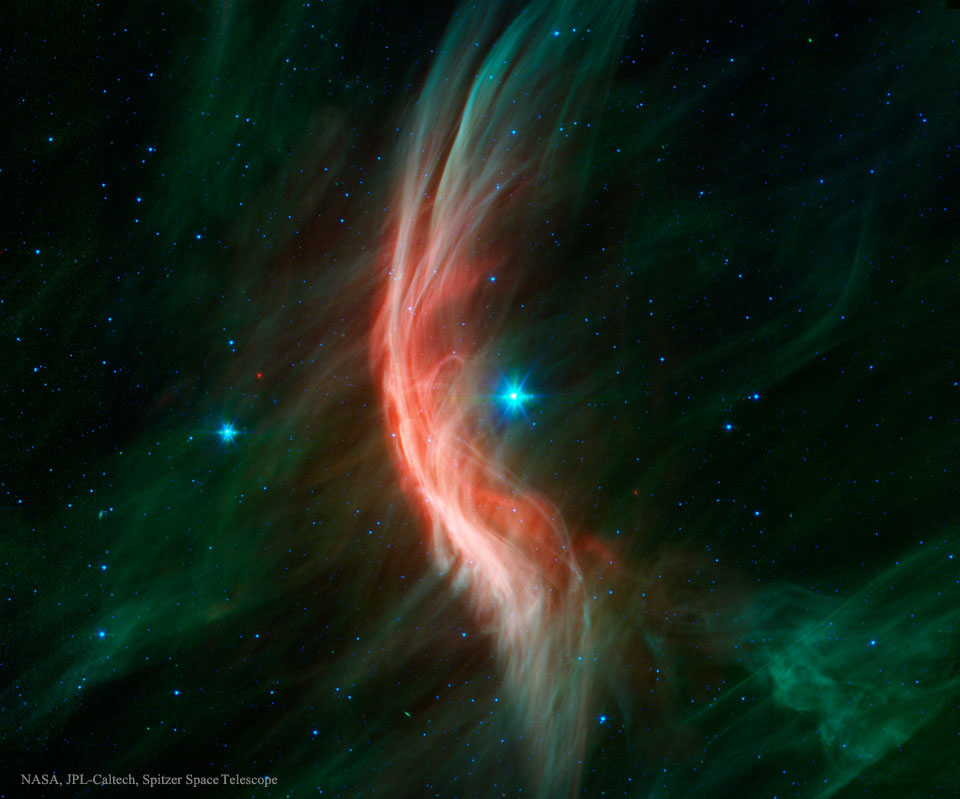
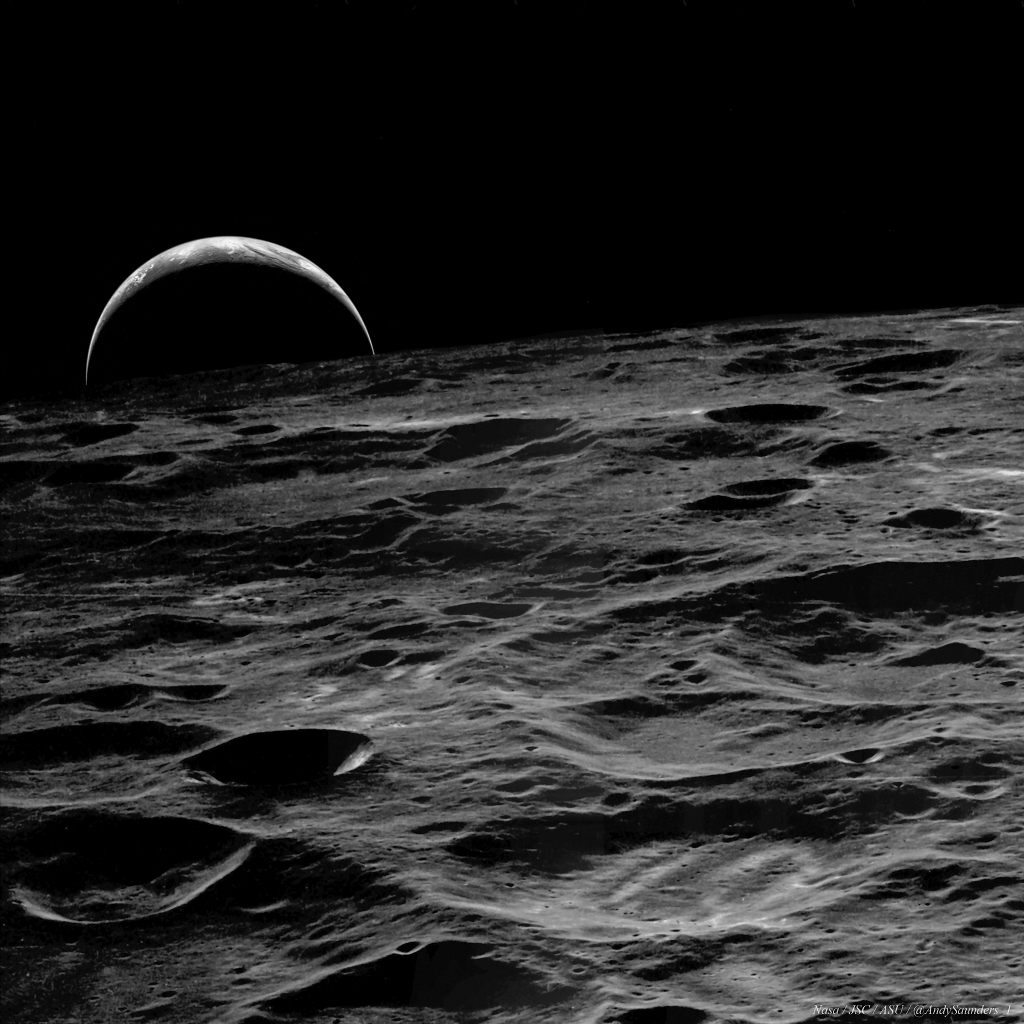
In 46 BC Julius Caesar reformed the calendar system. Based on advice by astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria, the Julian calendar included one leap day every four years to account for the fact that an Earth year is slightly more than 365 days long. In modern terms, the time it takes for the planet to orbit the Sun once is 365.24219 mean solar days. So if calendar years contained exactly 365 days they would drift from the Earth's year by about 1 day every 4 years and eventually July (named for Julius Caesar himself) would occur during the northern hemisphere winter. By adopting a leap year with an extra day every four years, the Julian calendar year would drift much less. In 1582 Pope Gregory XIII provided the further fine-tuning that leap days should not occur in years ending in 00, unless divisible by 400. This Gregorian Calendar system is the one in wide use today. Of course, tidal friction in the Earth-Moon system slows Earth's rotation and gradually lengthens the day by about 14 milliseconds per century. That means that leap days like today will not be necessary ... about 4 million years from now. via NASA https://ift.tt/39cQ9zs