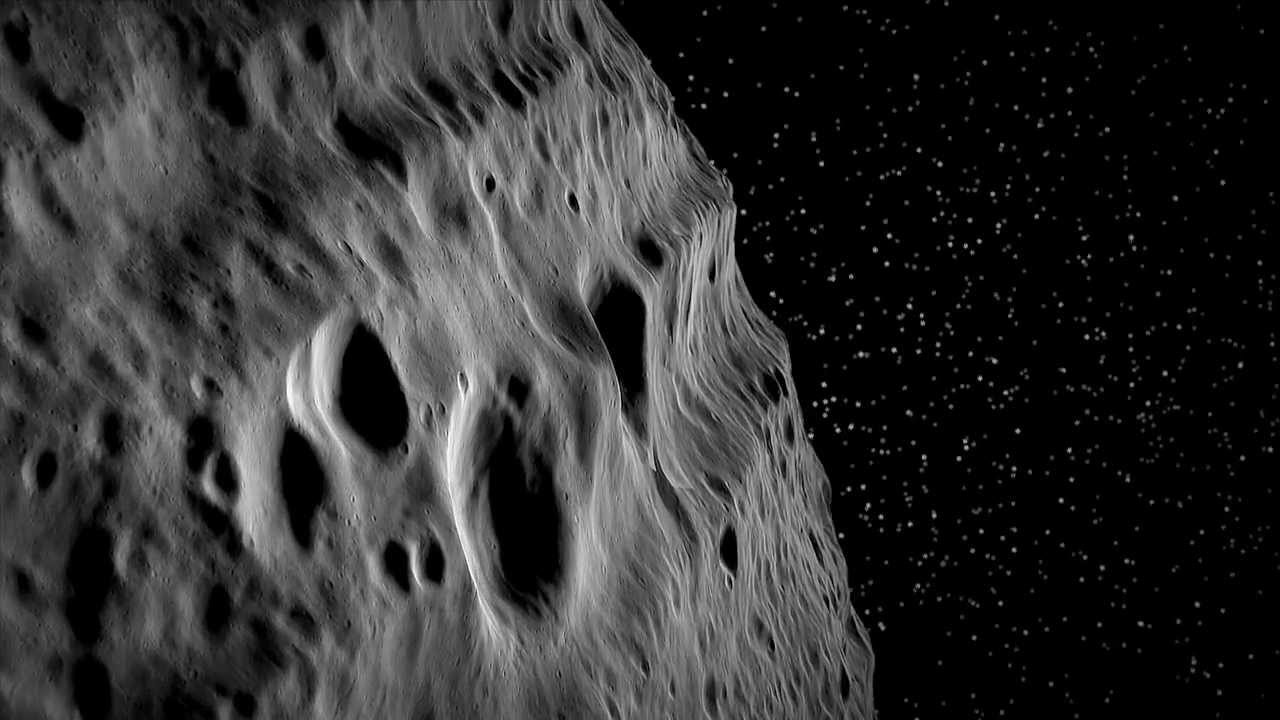
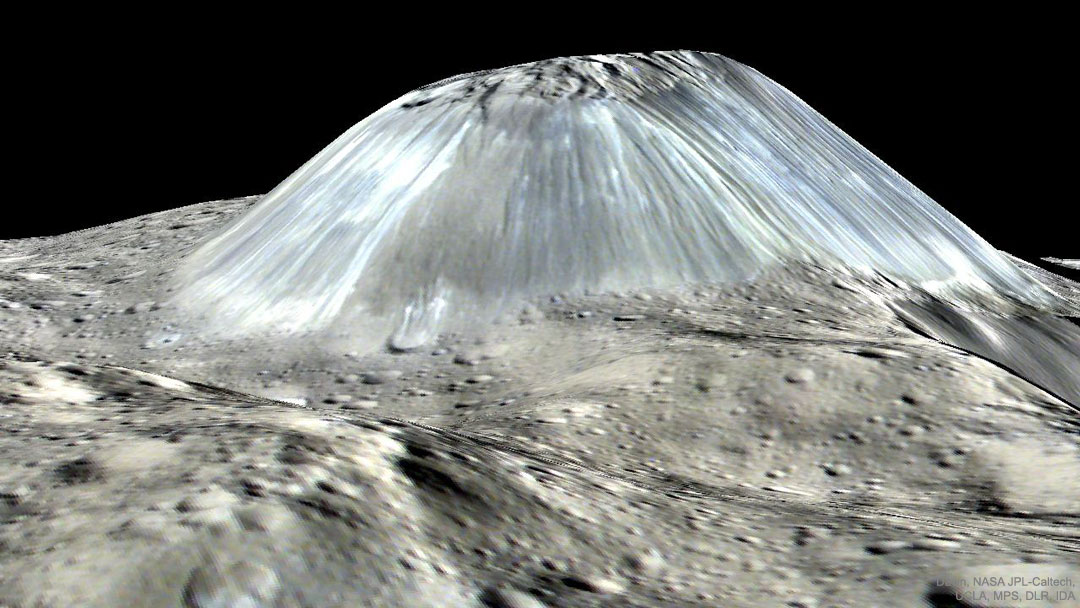
What would it be like to fly over the asteroid Vesta? Animators from the German Aerospace Center took actual images and height data from NASA's Dawn mission when it visited asteroid Vesta a few years ago and generated a virtual movie. The featured video begins with a sequence above Divalia Fossa, an unusual pair of troughs running parallel over heavily cratered terrain. Next, the virtual spaceship explores Vesta's 60-km Marcia Crater, showing numerous vivid details. Last, Dawn images were digitally recast with exaggerated height to better reveal Vesta's 5-km high mountain Aricia Tholus. The second largest object in the Solar System's asteroid belt, Vesta is the brightest asteroid visible from Earth and can be found with binoculars. Using Vesta Trek, you can explore all over Vesta yourself. via NASA https://ift.tt/2IYbQIw