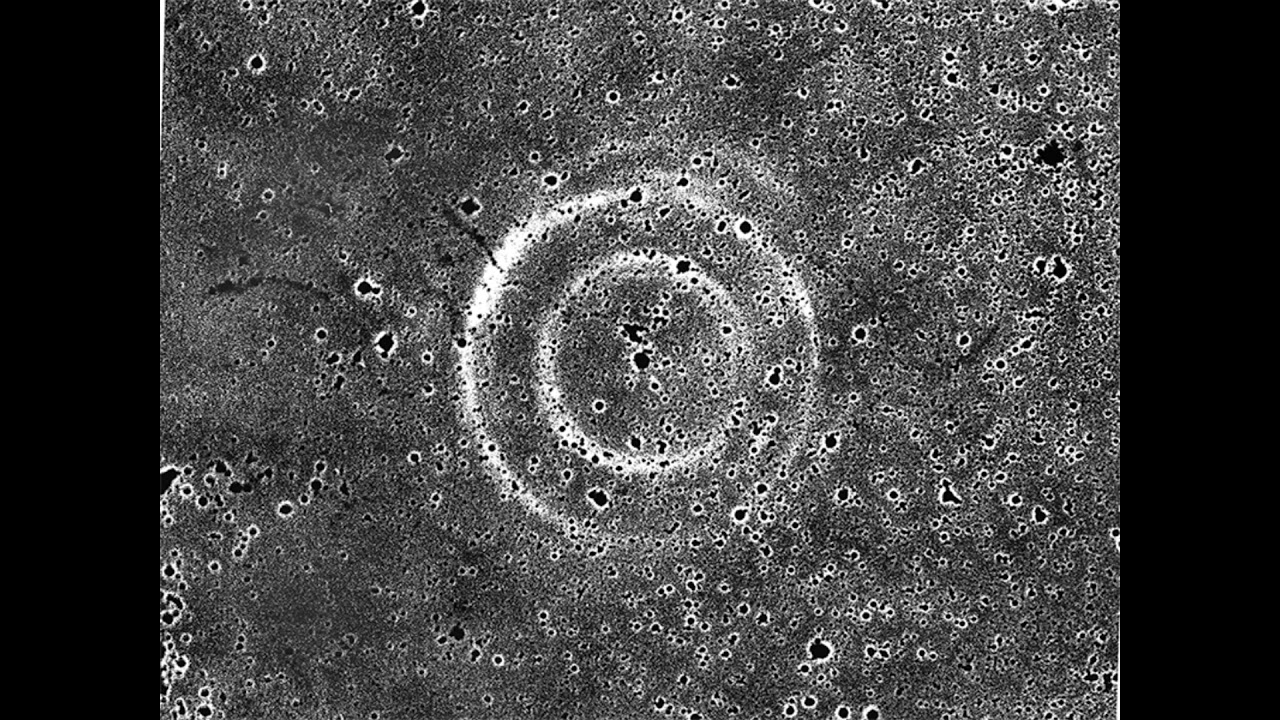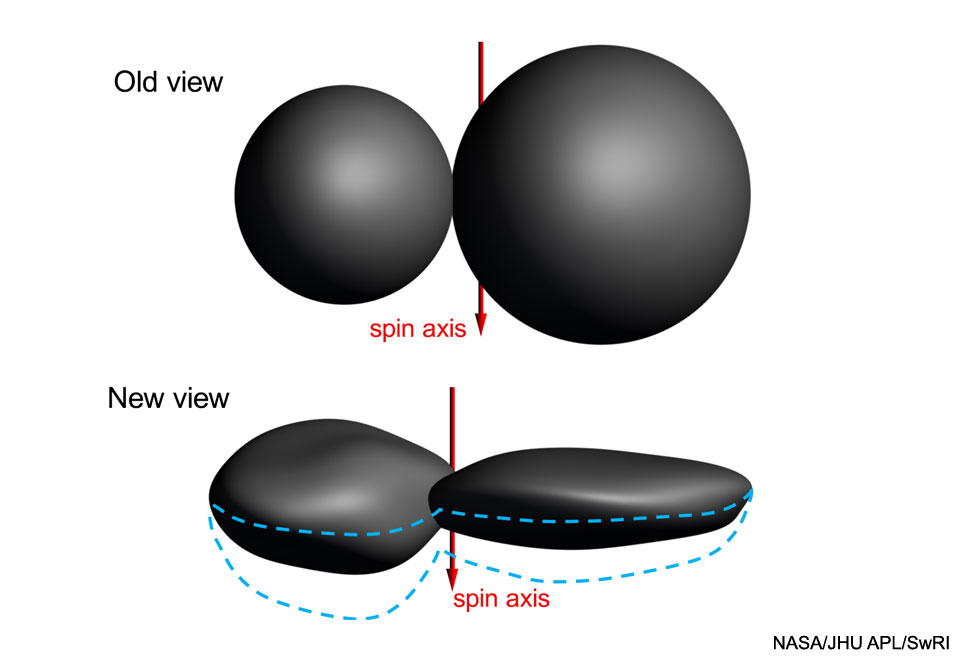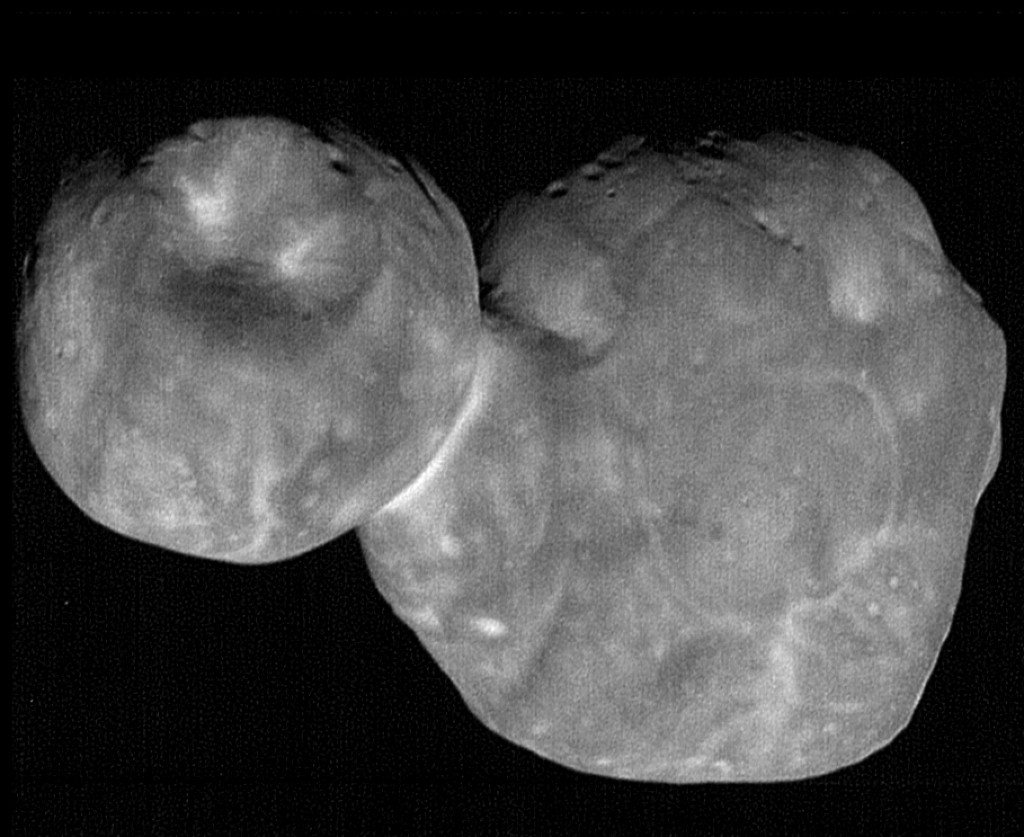
On January 1, New Horizons swooped to within 3,500 kilometers of the Kuiper Belt world known as Ultima Thule. That's about 3 times closer than its July 2015 closest approach to Pluto. The spacecraft's unprecedented feat of navigational precision, supported by data from ground and space-based observing campaigns, was accomplished 6.6 billion kilometers (over 6 light-hours) from planet Earth. Six and a half minutes before closest approach to Ultima Thule it captured the nine frames used in this composite image. The most detailed picture possible of the farthest object ever explored, the image has a resolution of about 33 meters per pixel, revealing intriguing bright surface features and dark shadows near the terminator. A primitive Solar System object, Ultima Thule's two lobes combine to span just 30 kilometers. The larger lobe, referred to as Ultima, is recently understood to be flattened like a fluffy pancake, while the smaller, Thule, has a shape that resembles a dented walnut. via NASA https://ift.tt/2UjlMQ4