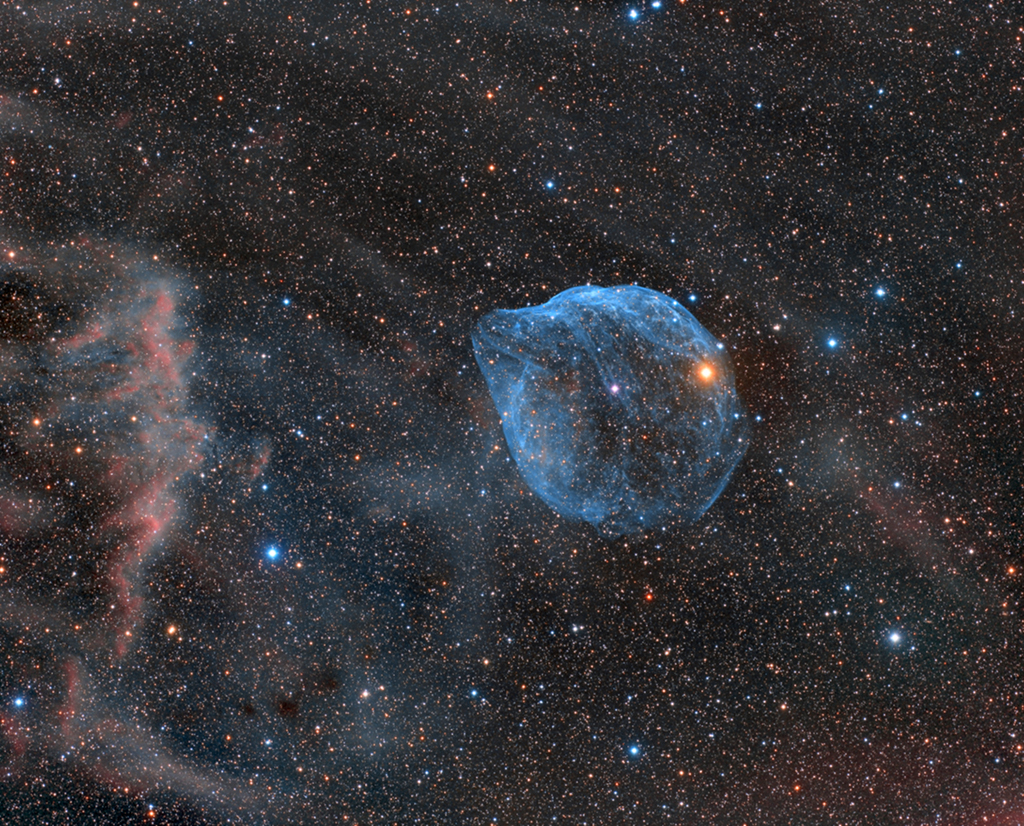
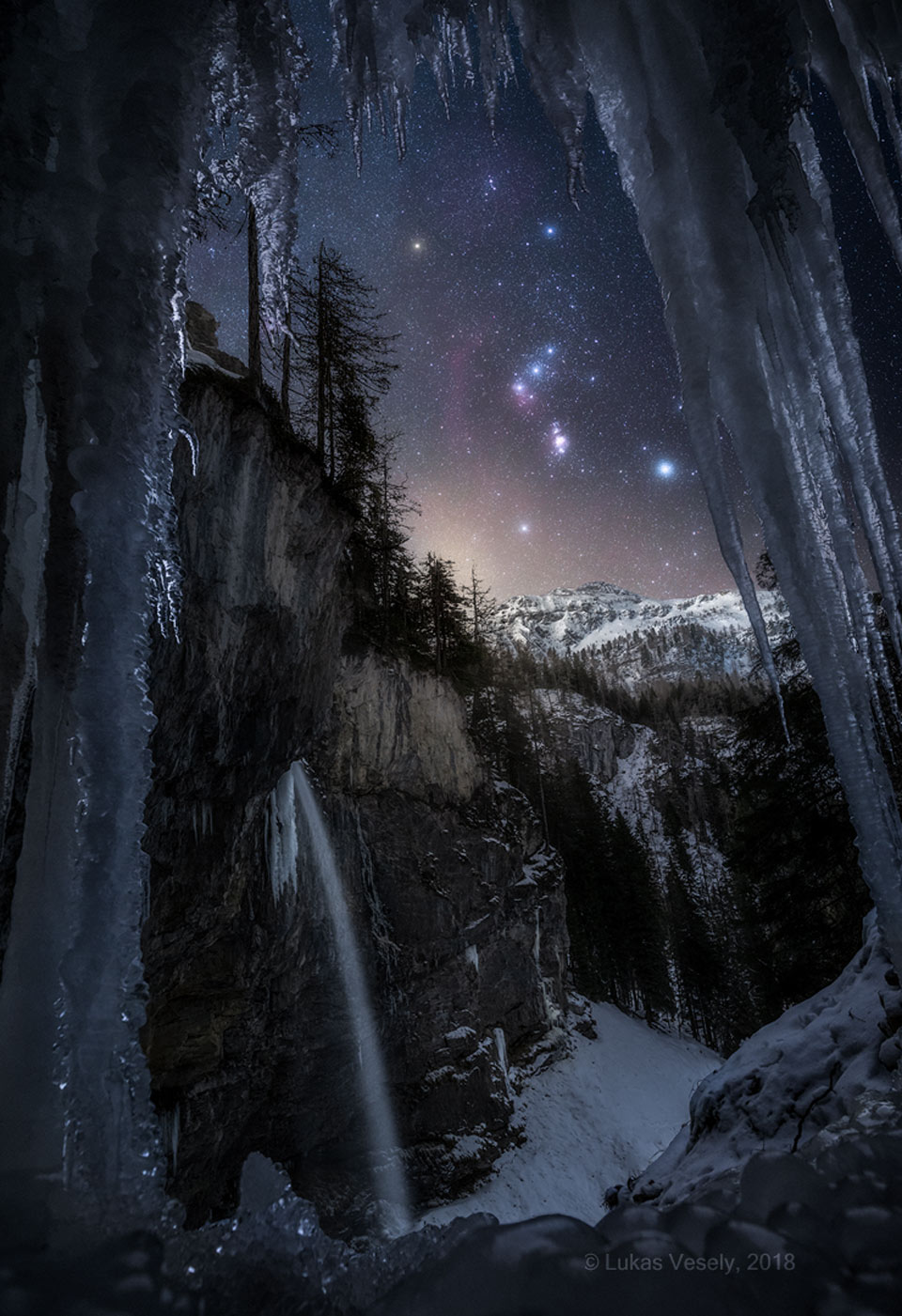
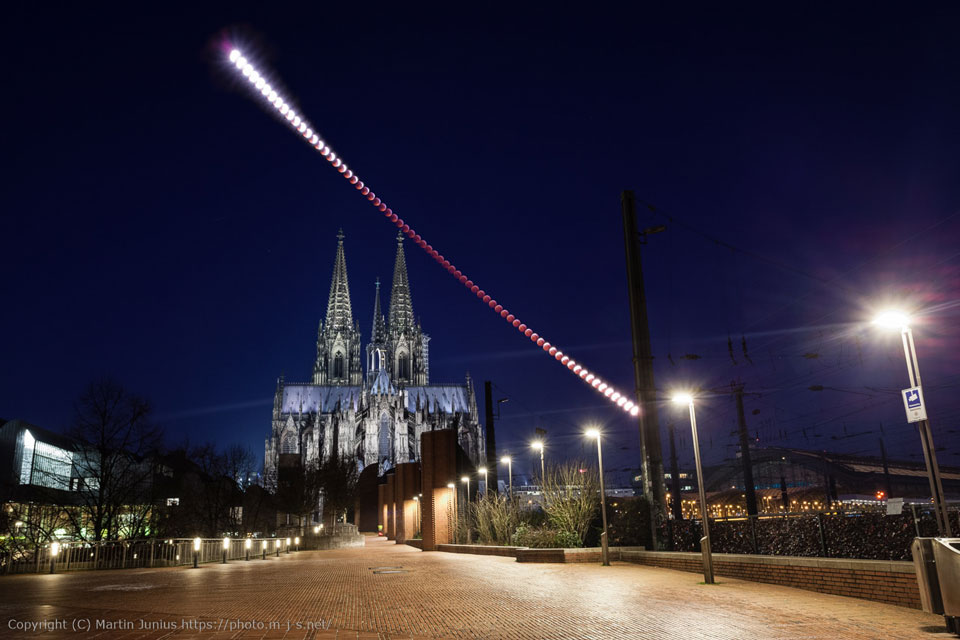
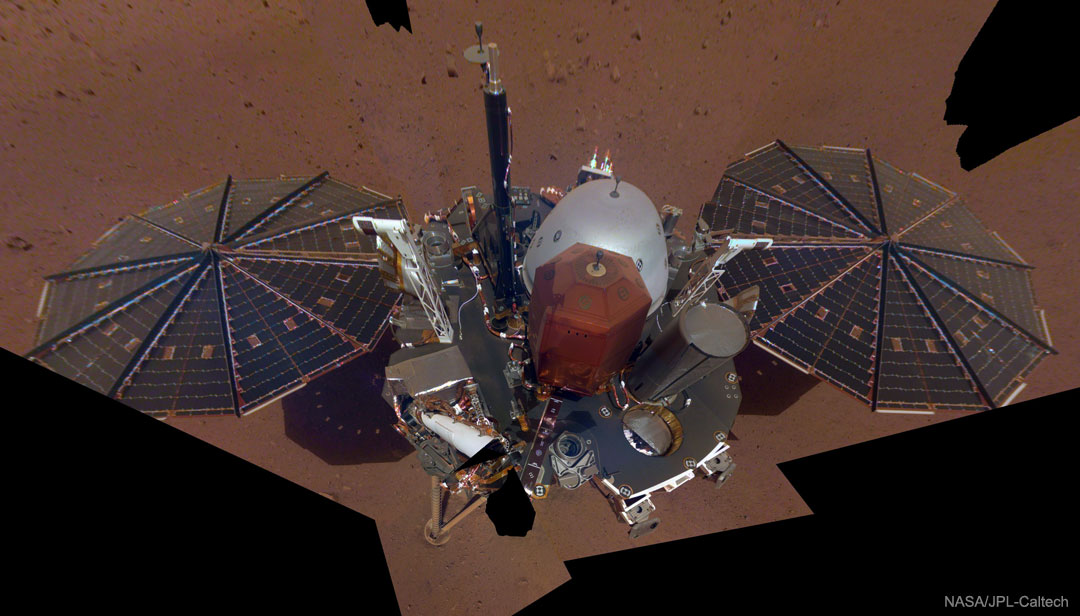
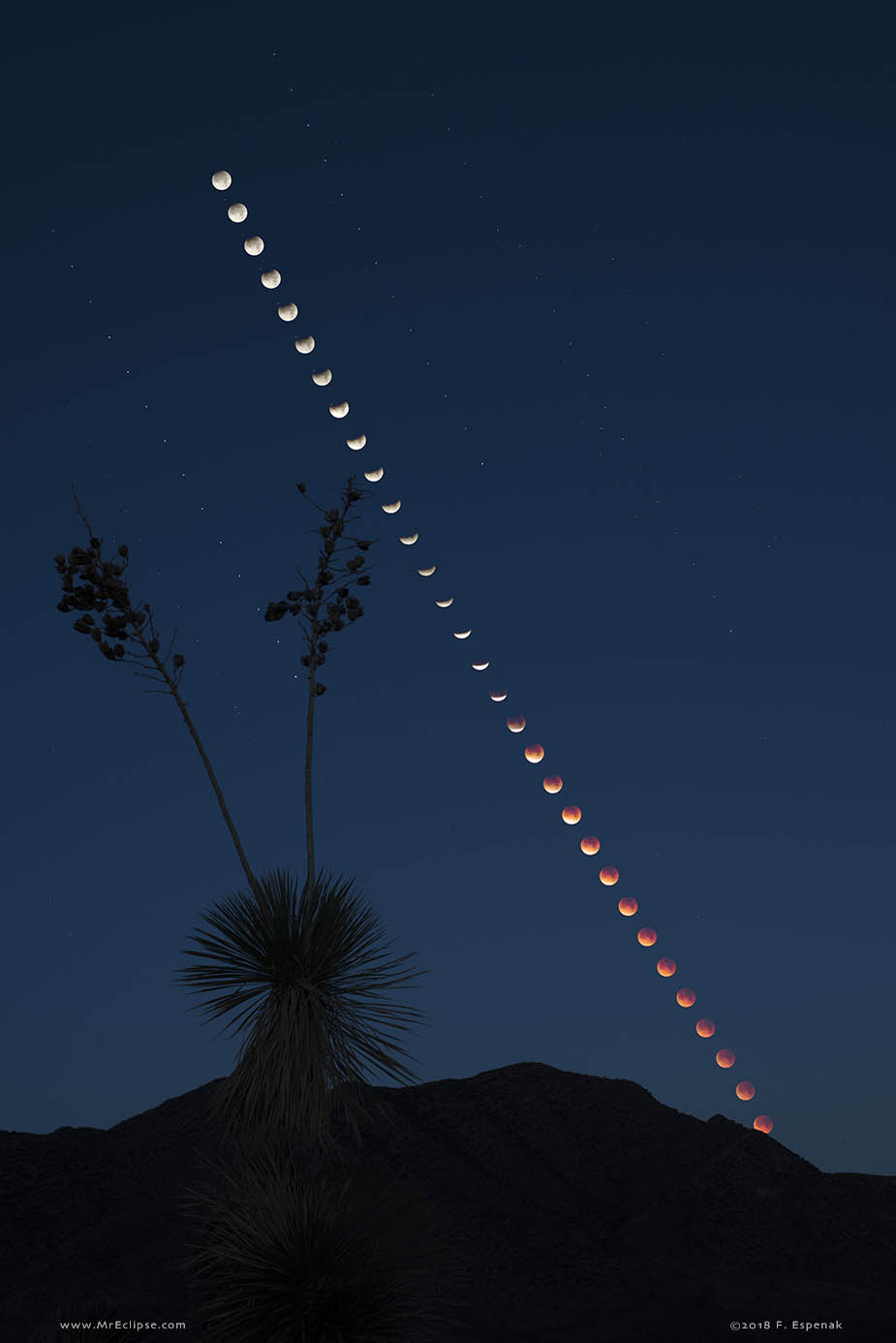
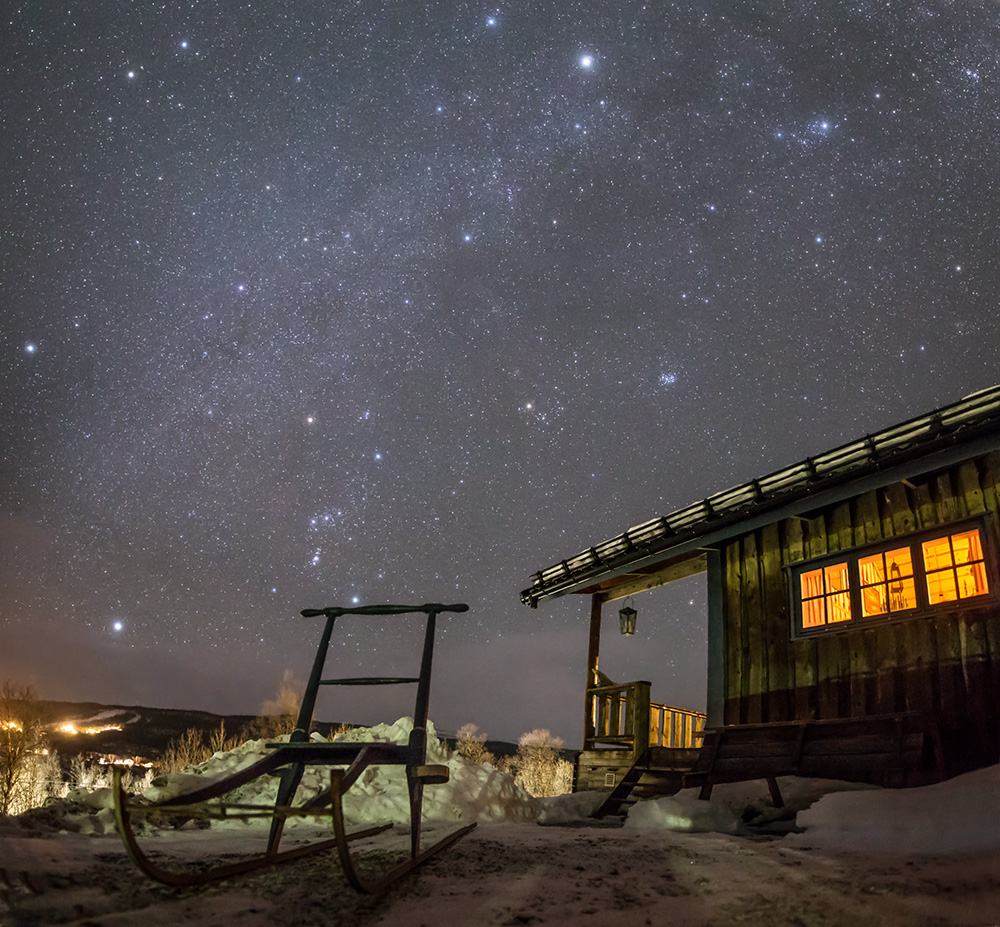
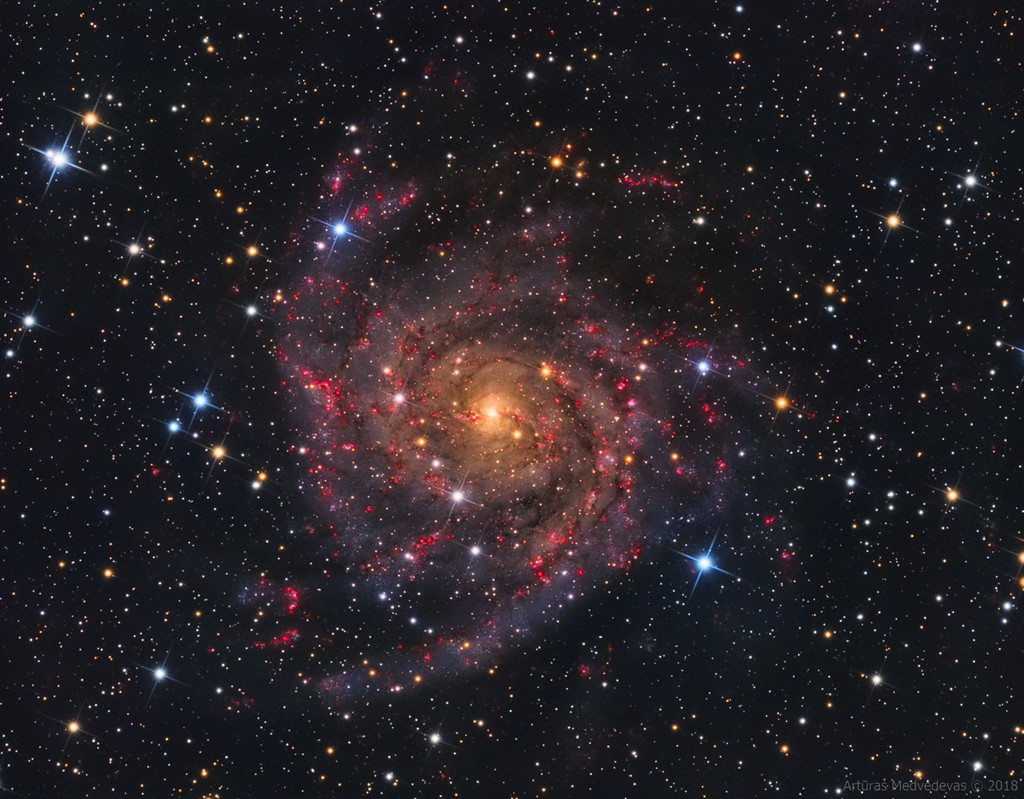
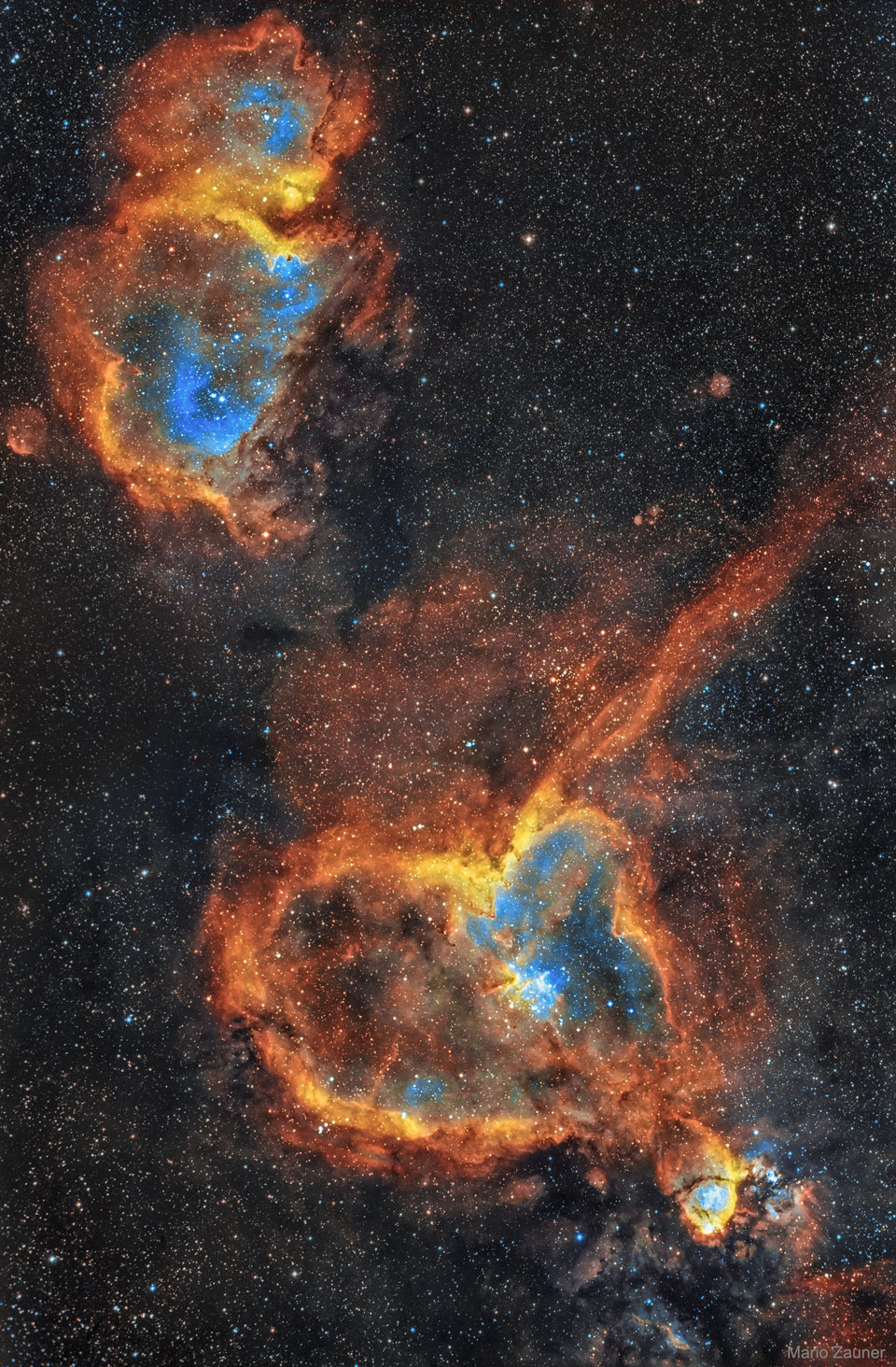
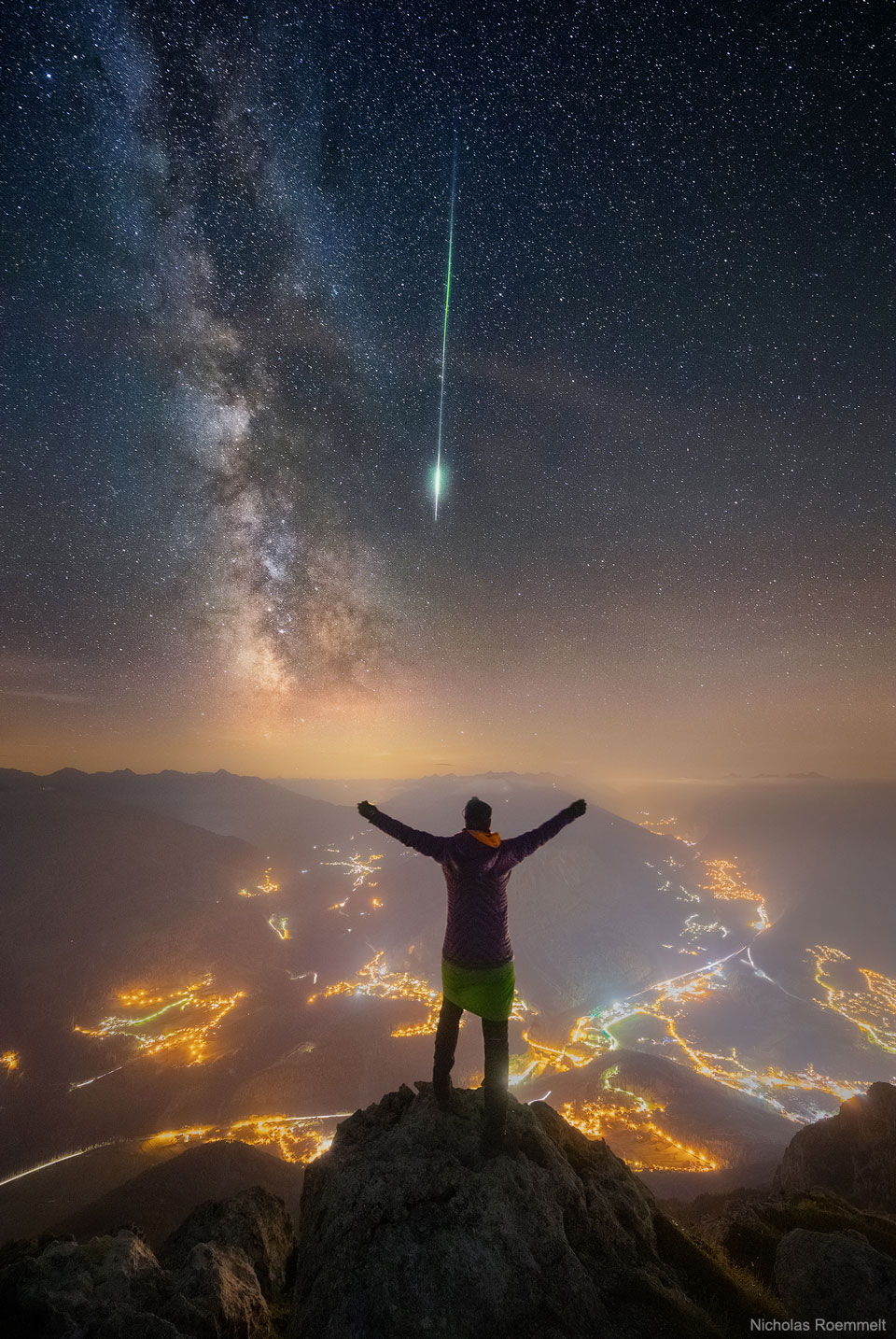
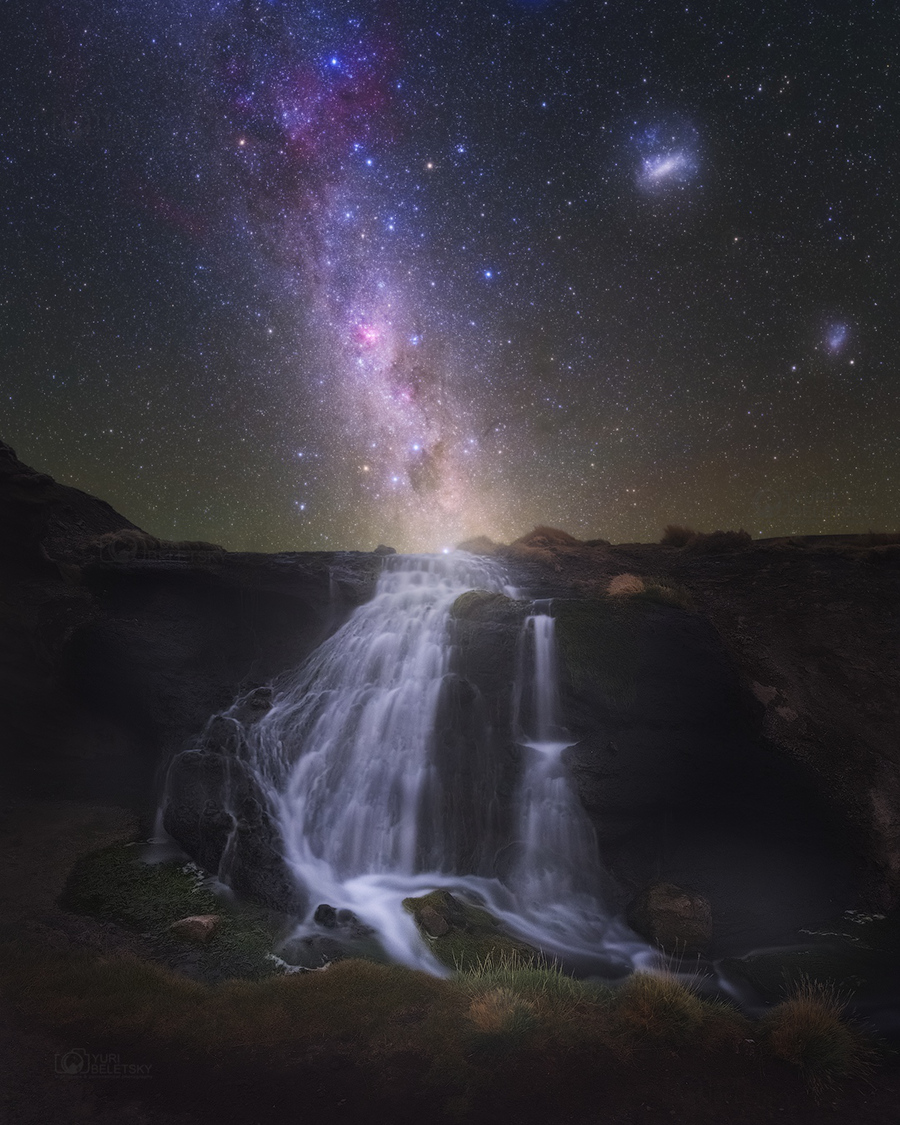
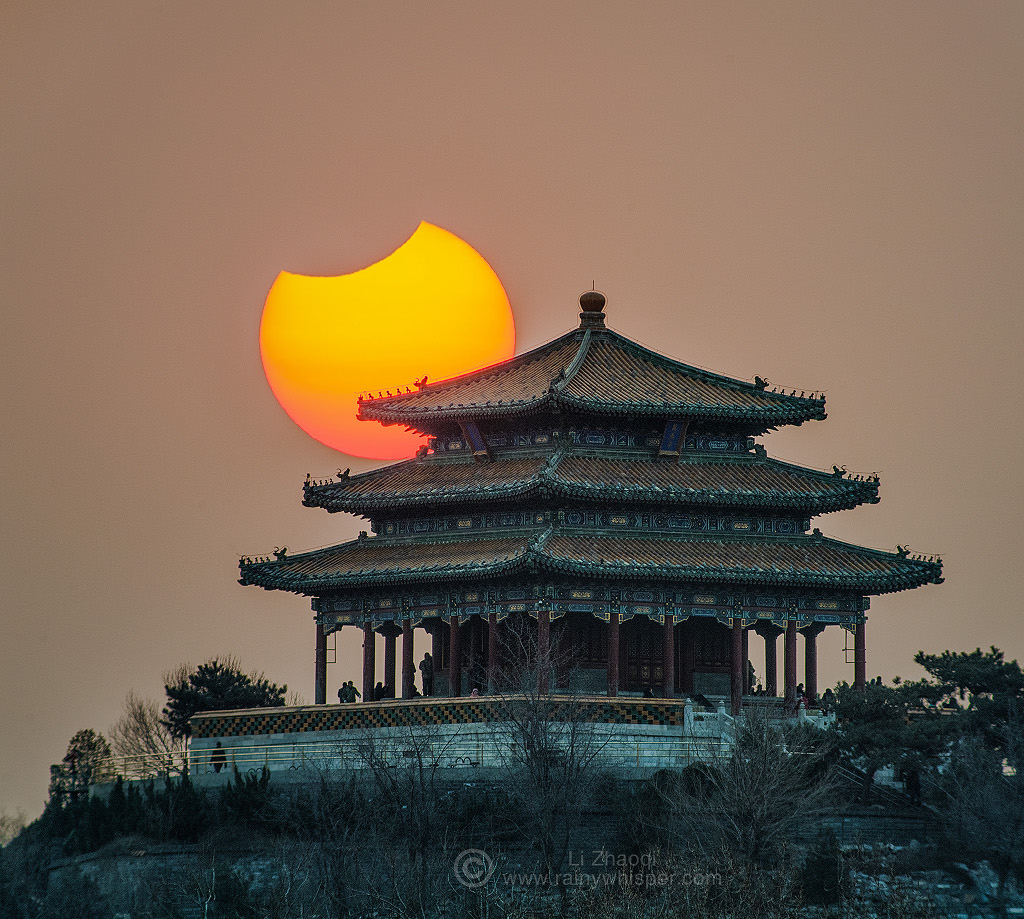
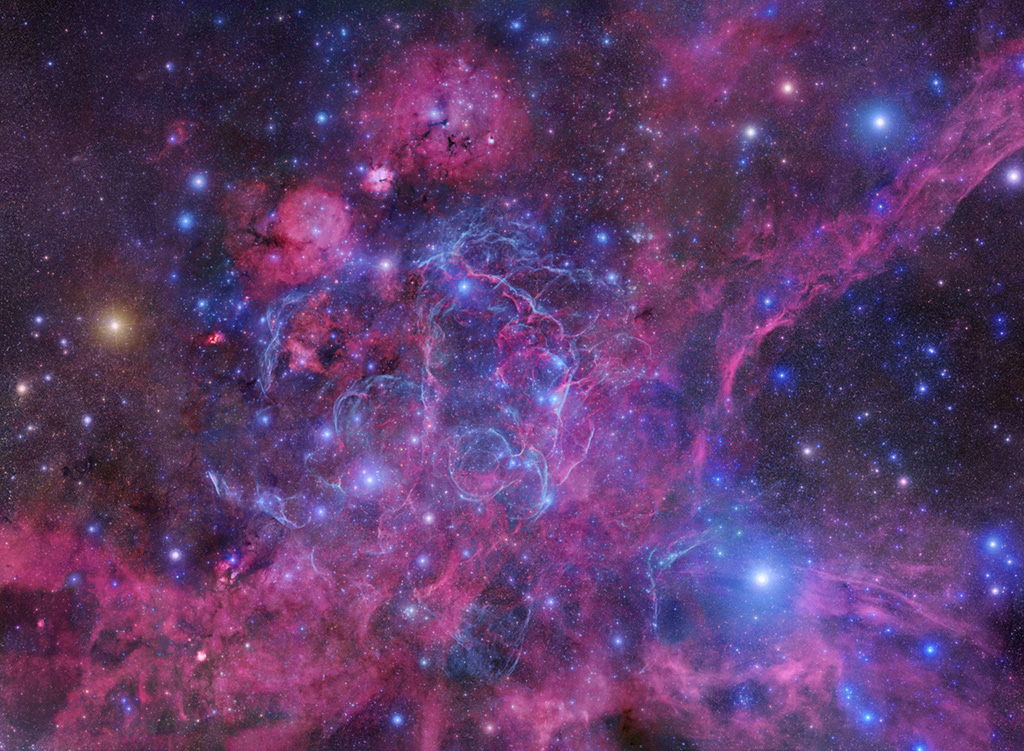
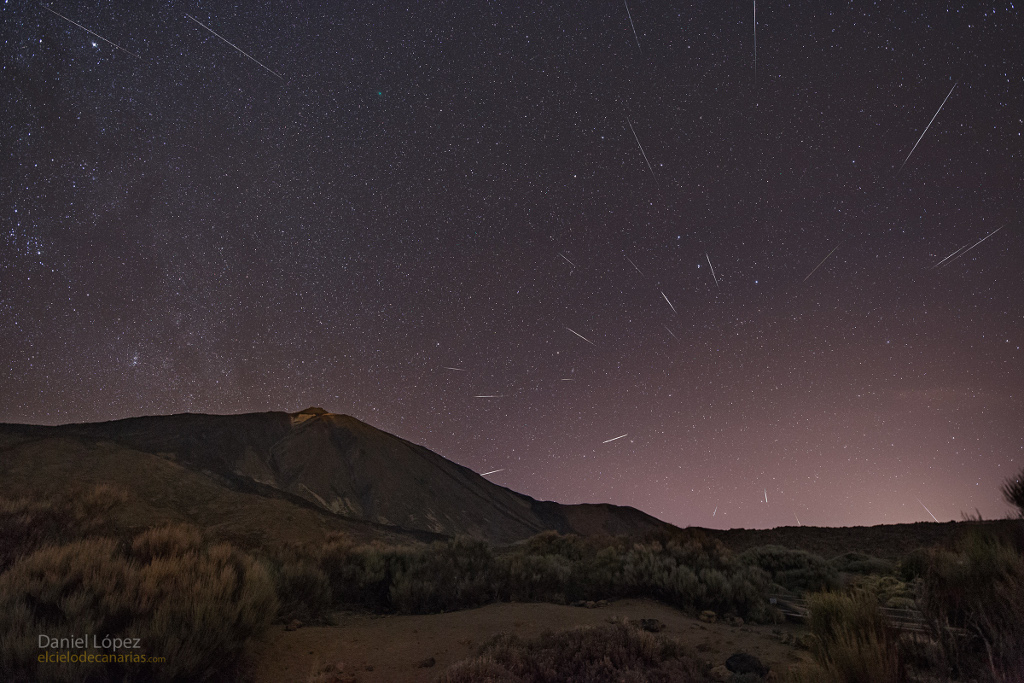
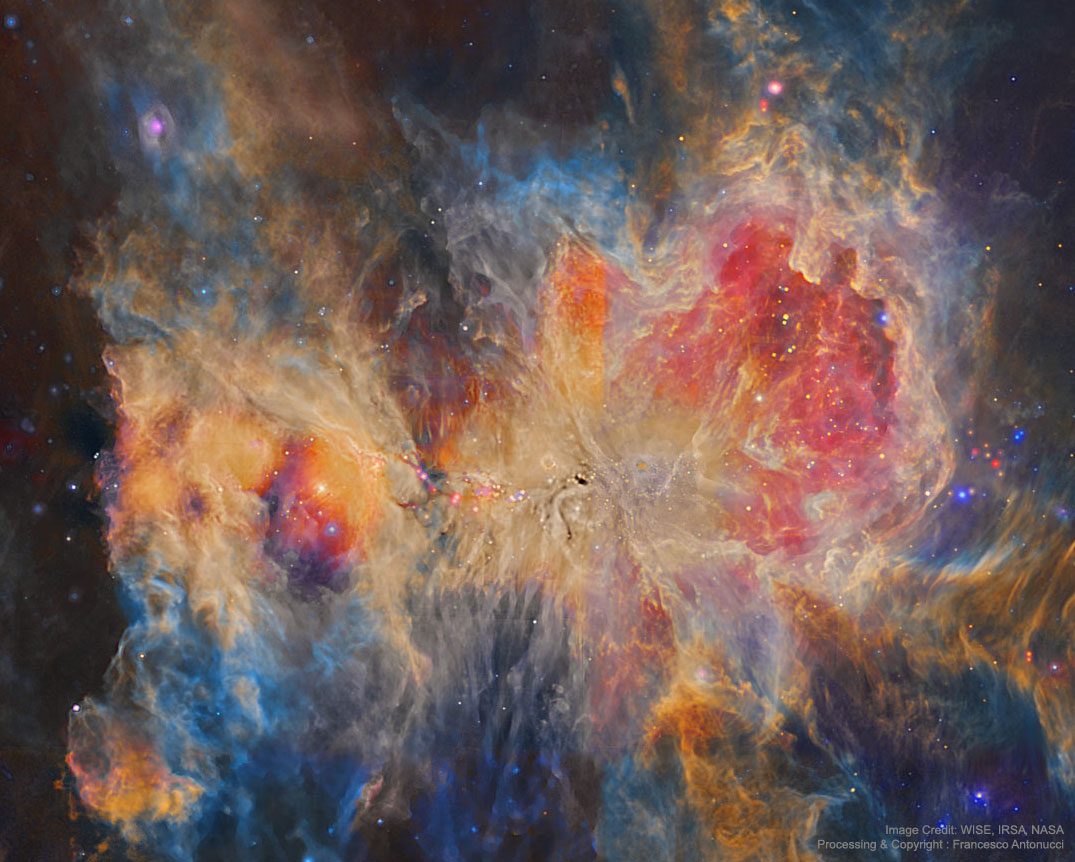
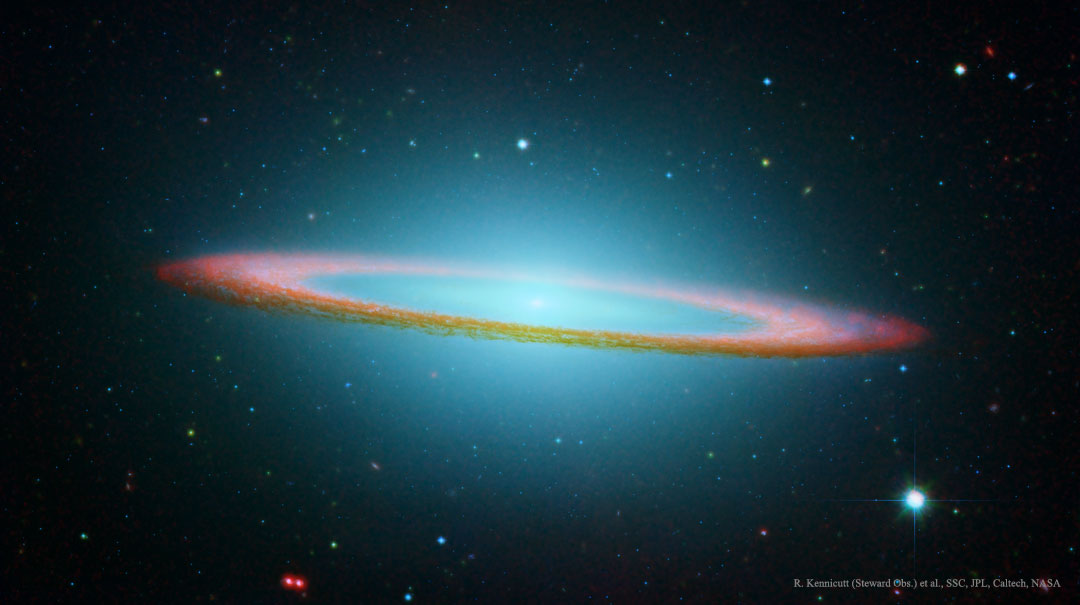
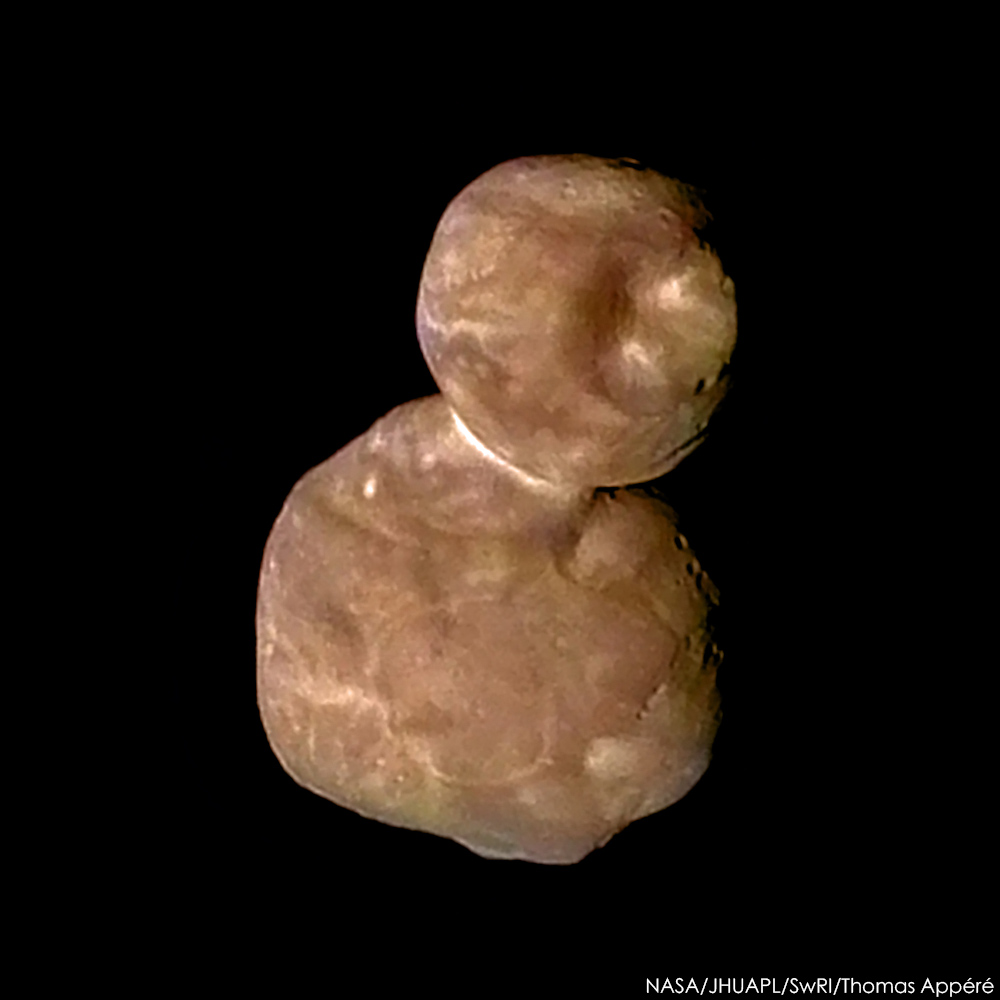
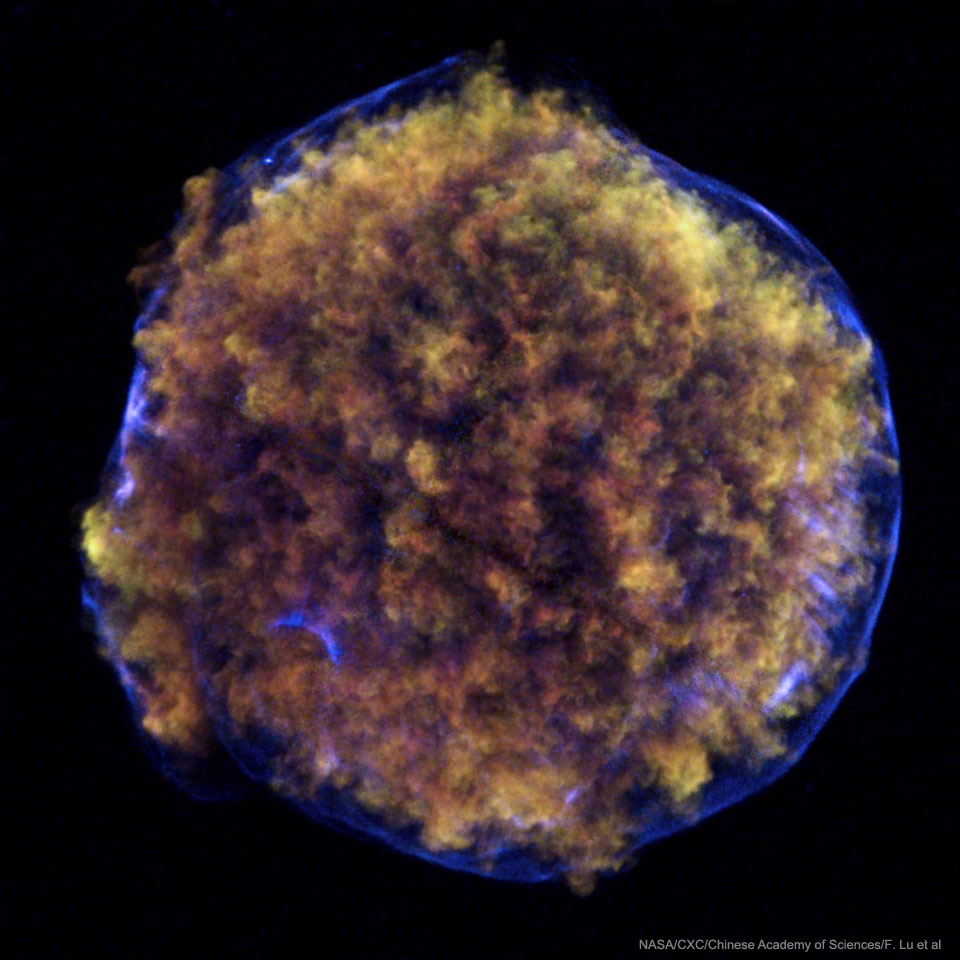
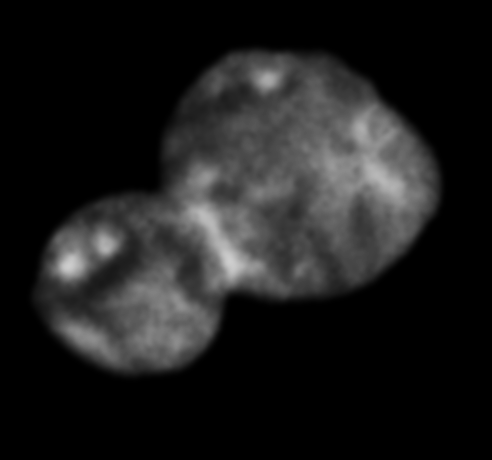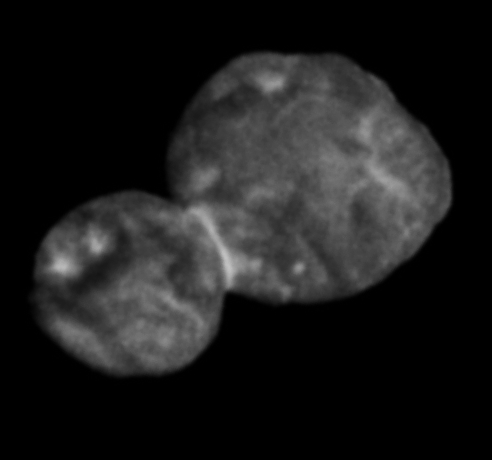
Blown by fast winds from a hot, massive star, this cosmic bubble is huge. Cataloged as Sharpless 2-308 it lies some 5,200 light-years away toward the constellation of the Big Dog (Canis Major) and covers slightly more of the sky than a Full Moon. That corresponds to a diameter of 60 light-years at its estimated distance. The massive star that created the bubble, a Wolf-Rayet star, is the bright one near the center of the nebula. Wolf-Rayet stars have over 20 times the mass of the Sun and are thought to be in a brief, pre-supernova phase of massive star evolution. Fast winds from this Wolf-Rayet star create the bubble-shaped nebula as they sweep up slower moving material from an earlier phase of evolution. The windblown nebula has an age of about 70,000 years. Relatively faint emission captured in the expansive image is dominated by the glow of ionized oxygen atoms mapped to a blue hue. SH2-308 is also known as The Dolphin Nebula. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2SfJfnB