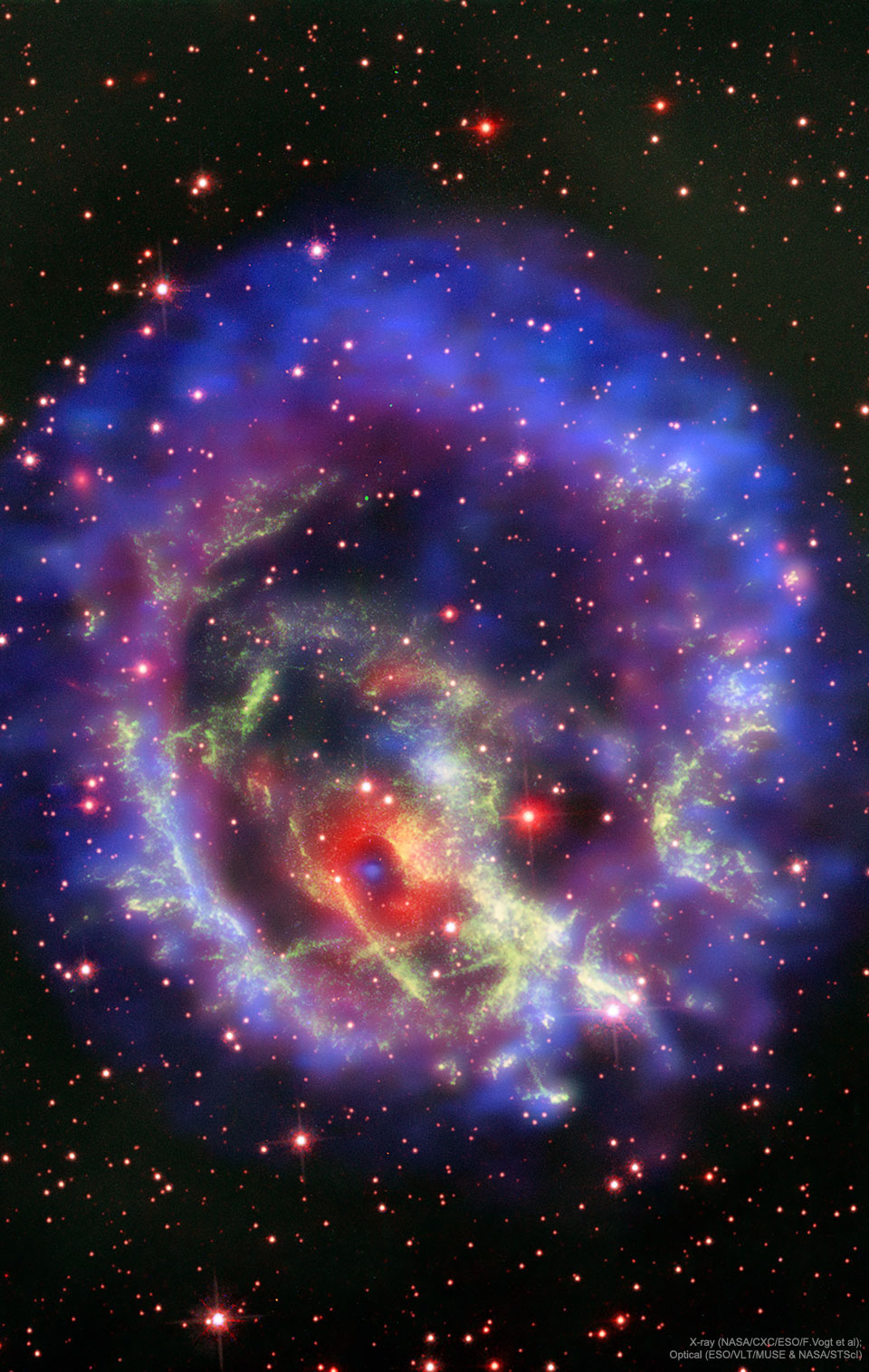
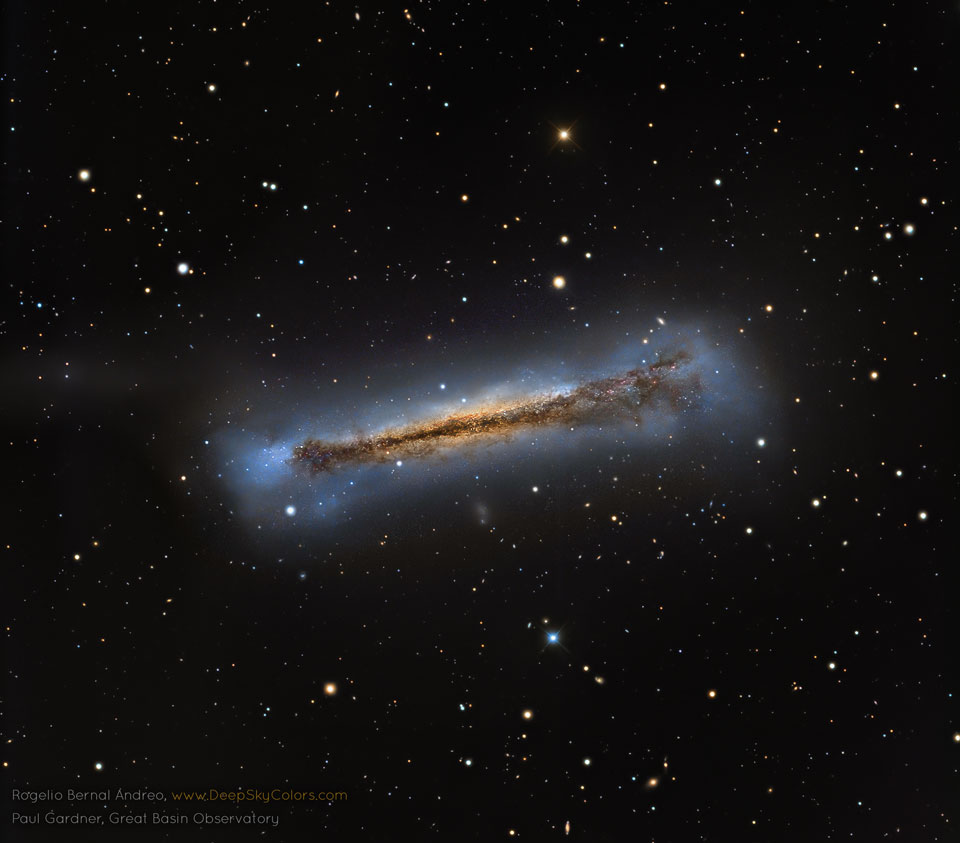
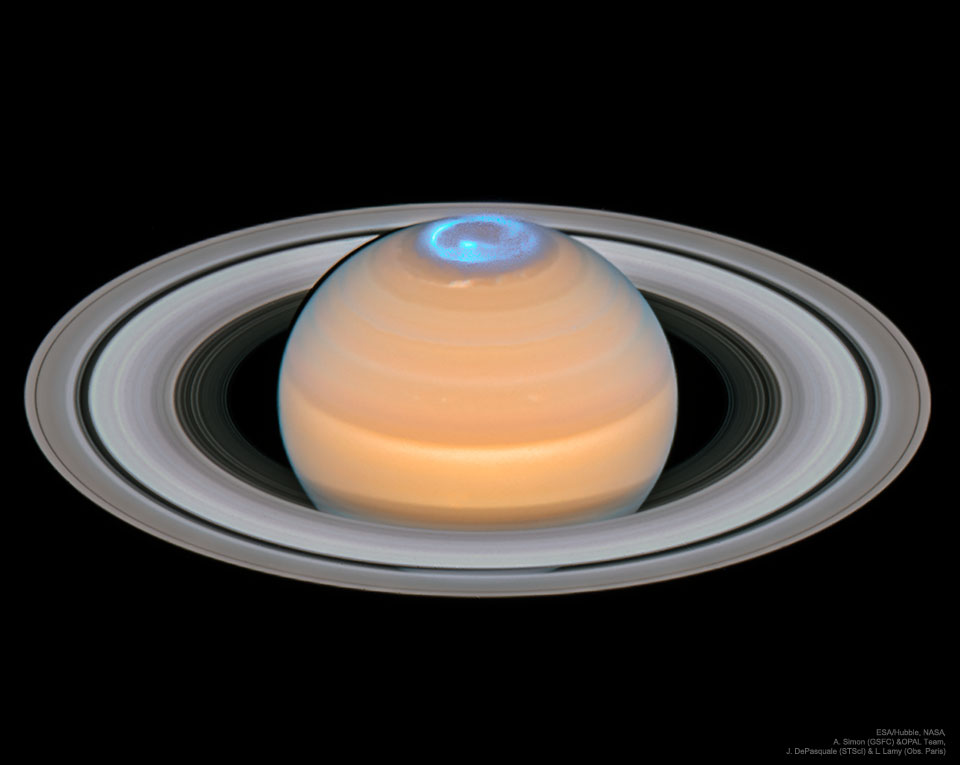
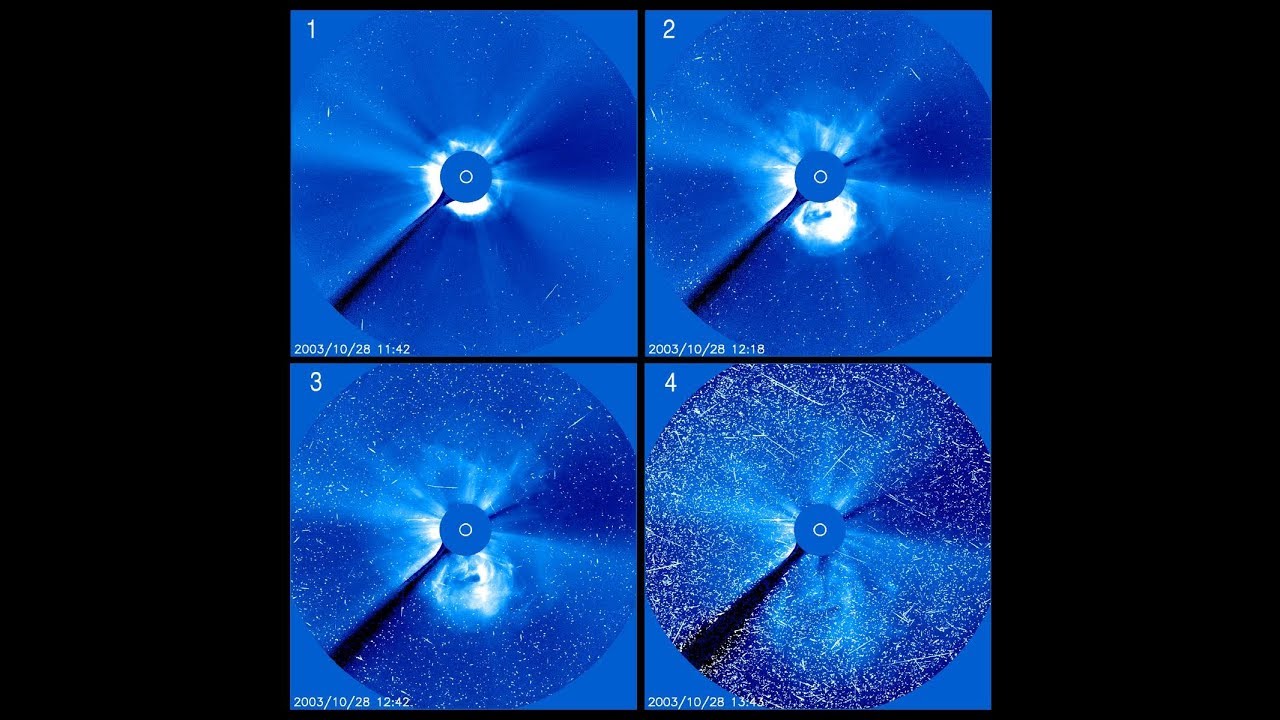
Why is this neutron star off-center? Recently a lone neutron star has been found within the debris left over from an old supernova explosion. The "lonely neutron star" in question is the blue dot at the center of the red nebula near the bottom left of E0102-72.3. In the featured image composite, blue represents X-ray light captured by NASA's Chandra Observatory, while red and green represent optical light captured by ESO's Very Large Telescope in Chile and NASA's Hubble Space Telescope in orbit. The displaced position of this neutron star is unexpected since the dense star is thought to be the core of the star that exploded in the supernova and created the outer nebula. It could be that the neutron star in E0102 was pushed away from the nebula's center by the supernova itself, but then it seems odd that the smaller red ring remains centered on the neutron star. Alternatively, the outer nebula could have been expelled during a different scenario -- perhaps even involving another star. Future observations of the nebulas and neutron star appear likely to resolve the situation. via NASA https://ift.tt/2DDSt7b