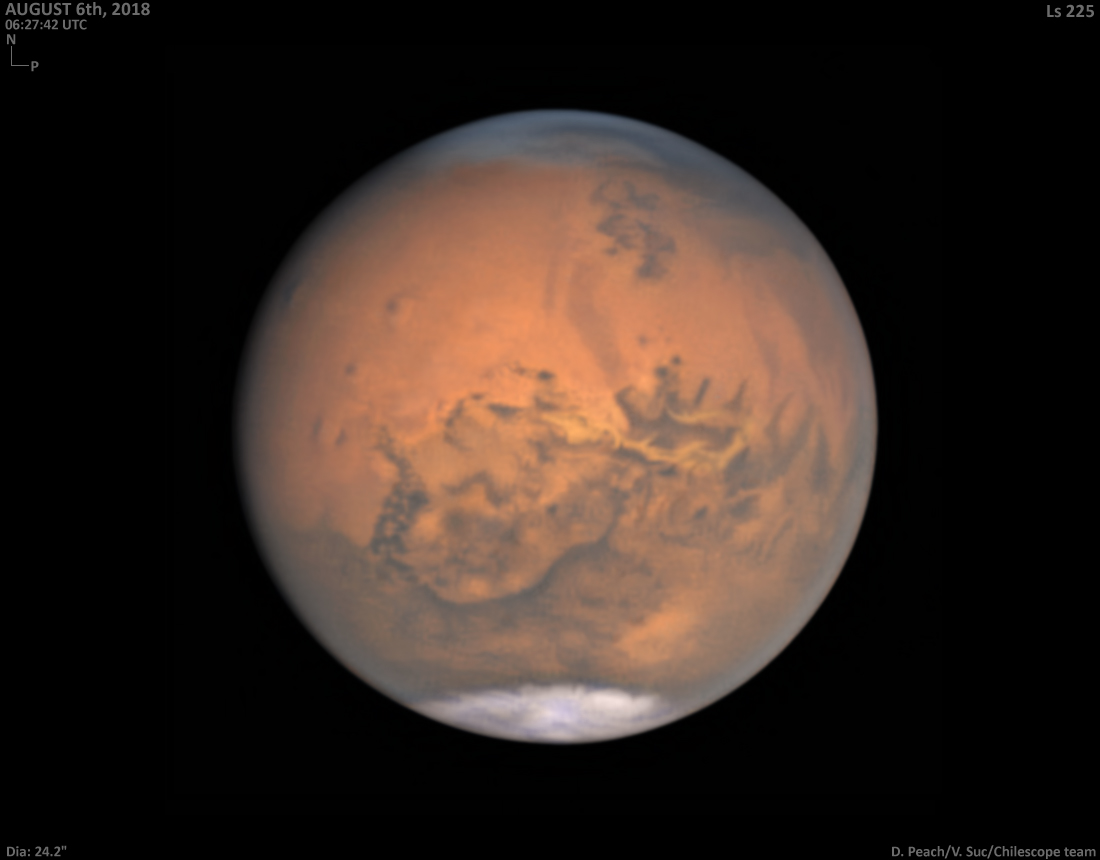
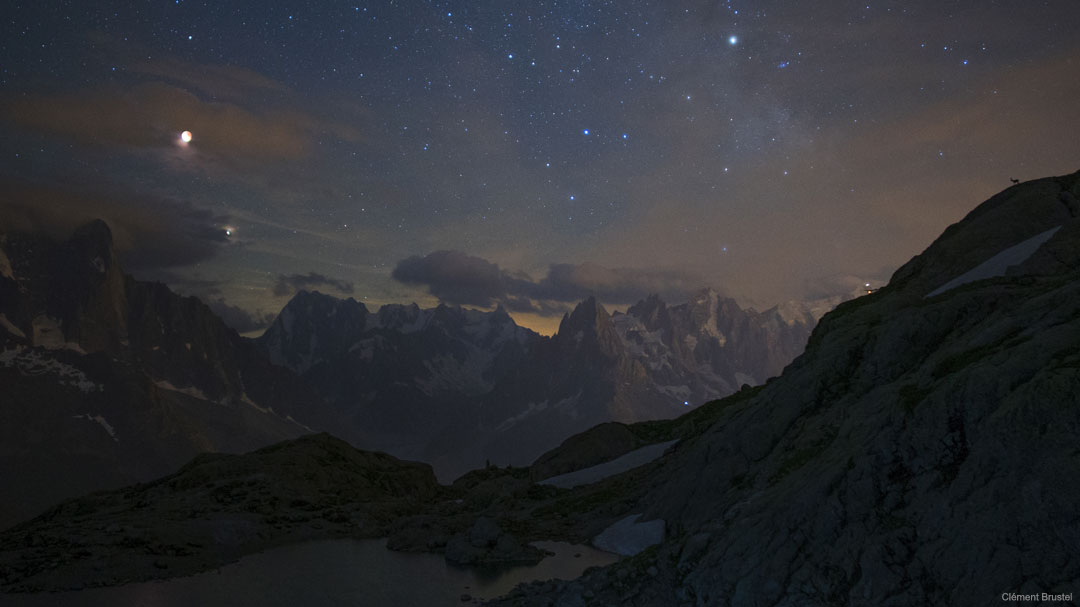
Still bright in evening skies, Mars was just past opposition and closest to Earth on July 31, a mere 57.6 million kilometers away. Captured only a week later, this remarkable image shows the Red Planet's disk near its maximum size in earthbound telescopes, but still less than 1/74th the apparent diameter of a Full Moon. Broad regional surface shadings are starting to reappear in the tantalizing view as the latest planet-wide dust storm subsides. With the bright south polar cap at the bottom, the Valles Marineris extends along the center of the disk. Just below it lies the roughly circular Solis Lacus region sometimes known as the Eye of Mars. In a line, three prominent dark spots left of center are the volcanic Tharsis Montes. via NASA https://ift.tt/2oqFPhw