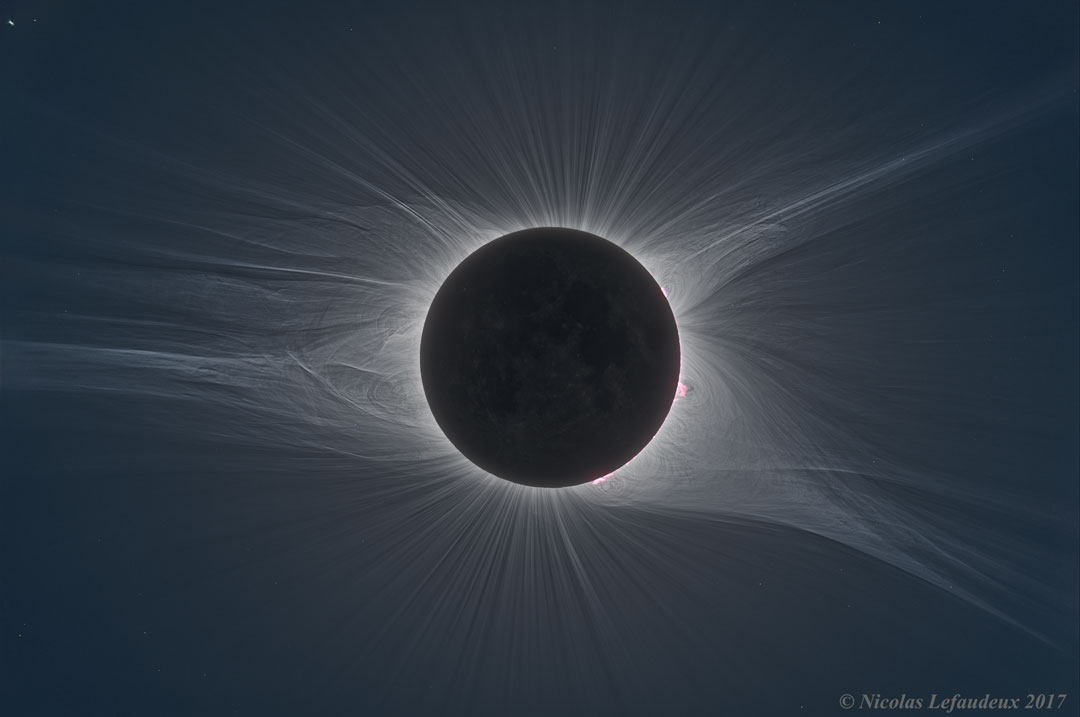
How great was the Great American Eclipse? The featured HDR image shows it to be perhaps greater than we knew. On August 21 of last year, the Moon blocked the Sun for a few minutes along a narrow path across the USA. Although one of the most photographed events in human history, this image -- only recently completed after an extraordinary amount of digital processing -- shows one of the most detailed depictions of a solar corona ever taken. Composed of extremely hot gas, the solar corona is only visible to the unaided eye during a total solar eclipse. The featured image combined over 70 images of different time exposures. The series of complementary HDR images recovered enough detail to see motion of the solar corona. The images were taken in Unity, Oregon in the morning to get steady atmospheric seeing conditions. The next total solar eclipse visible on Earth will be in 2019 July, while the next one visible across North America and the USA will occur in 2024 April. via NASA https://ift.tt/2jhCWgq