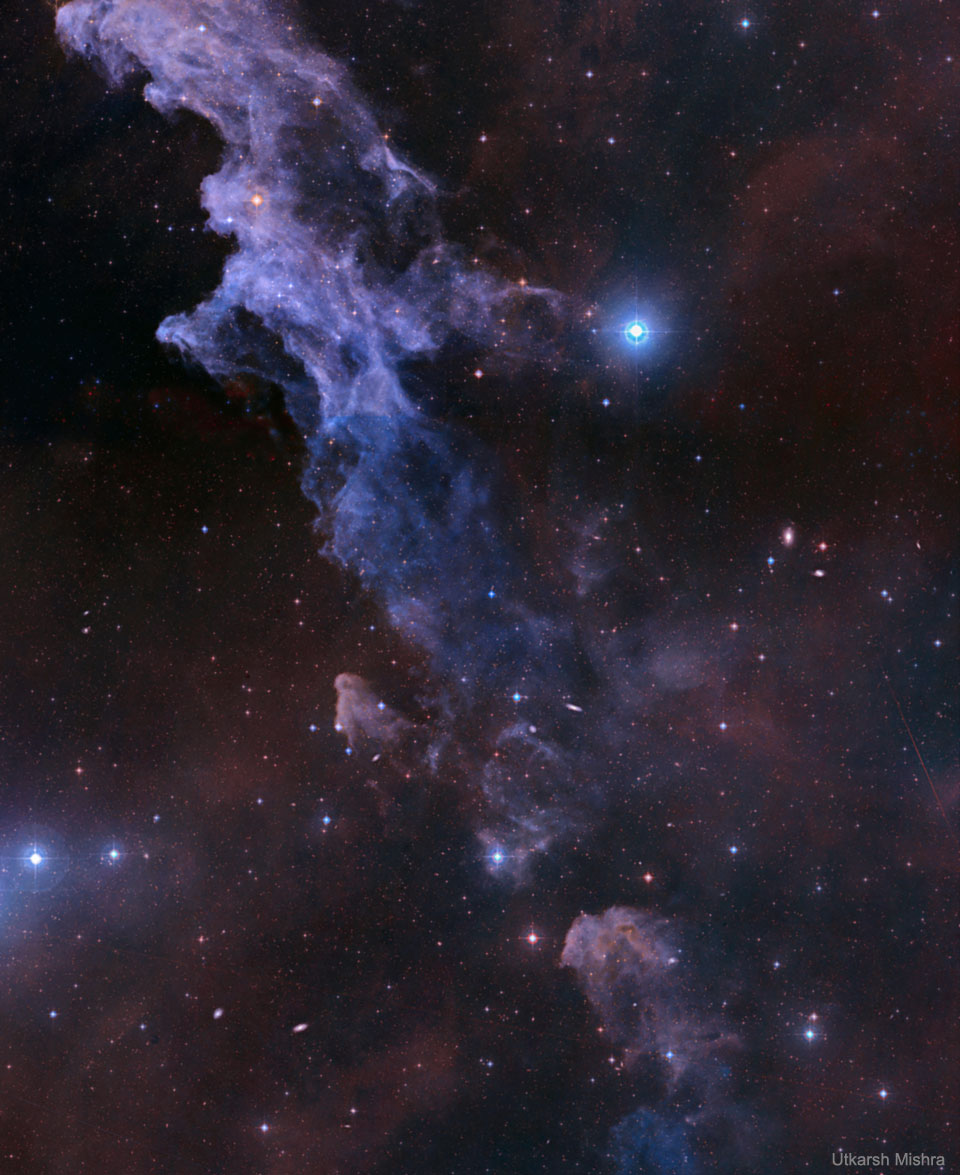
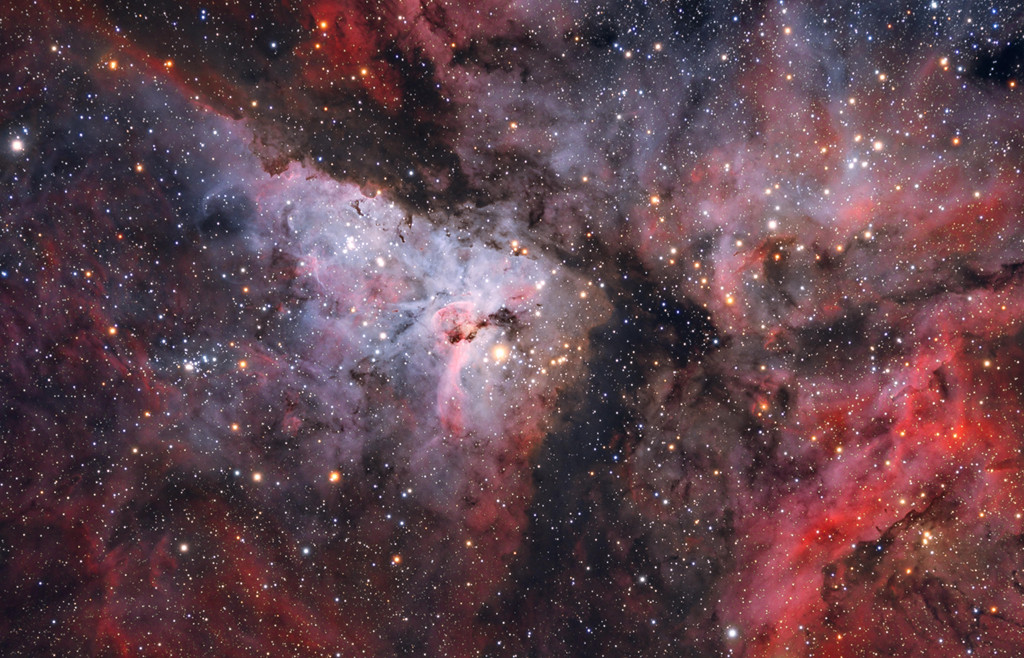
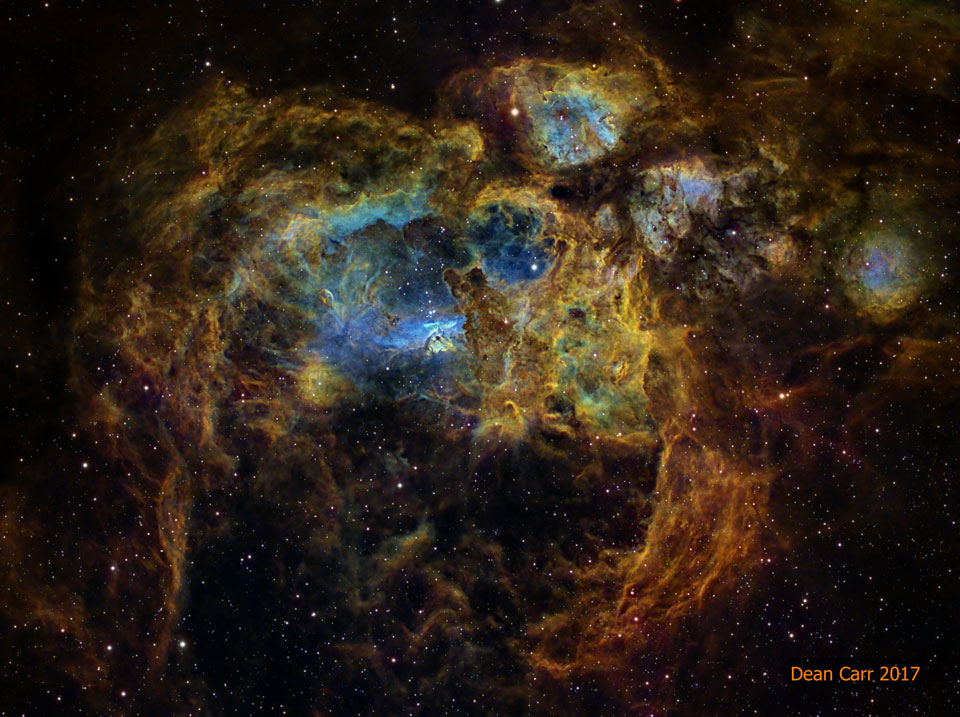
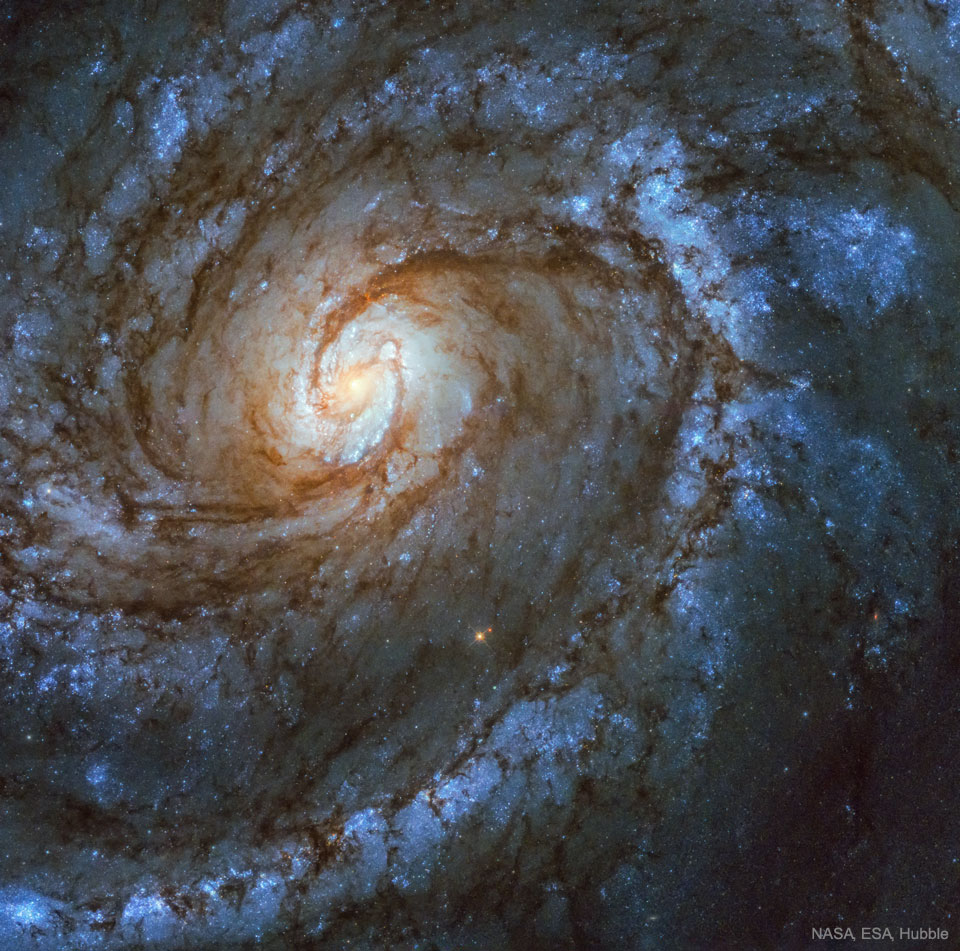
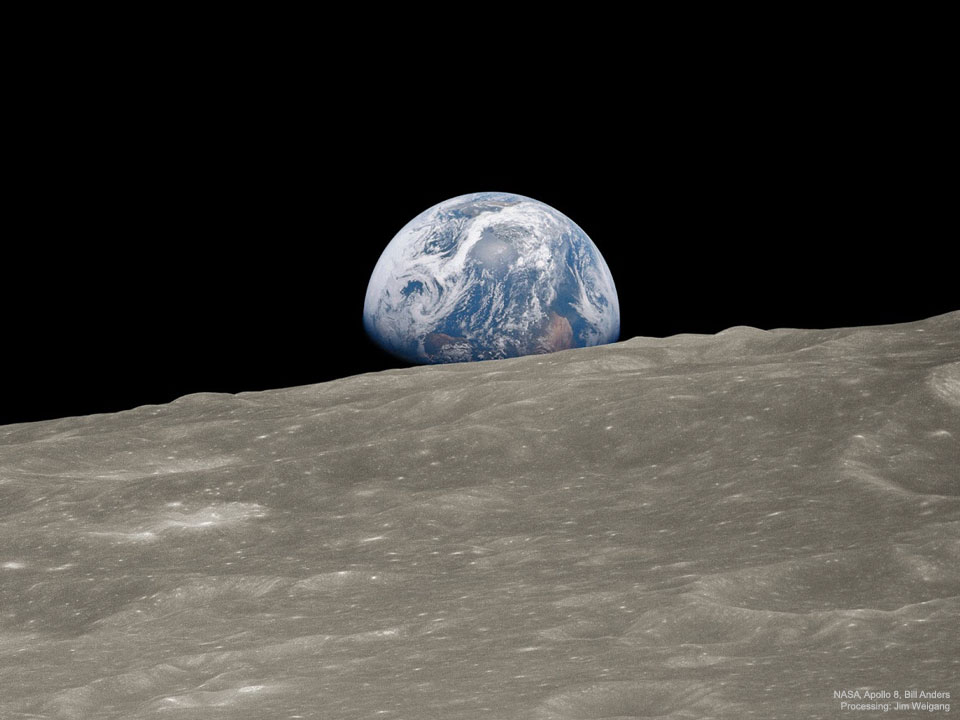
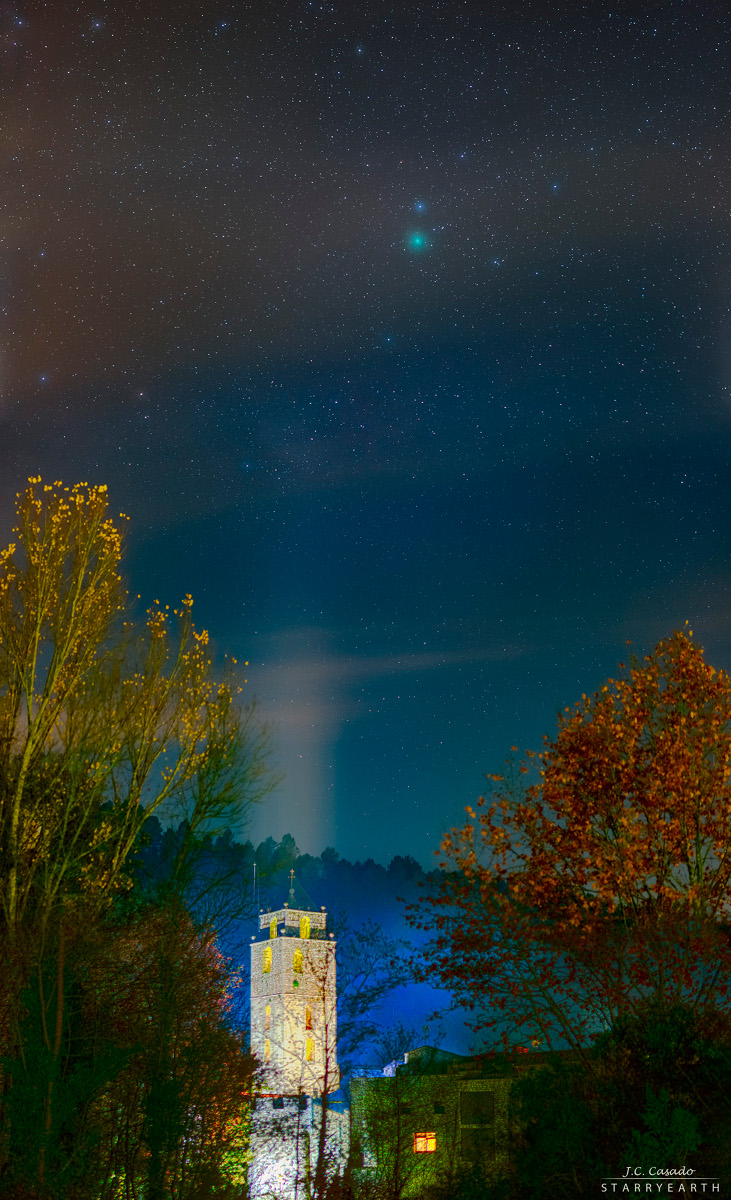
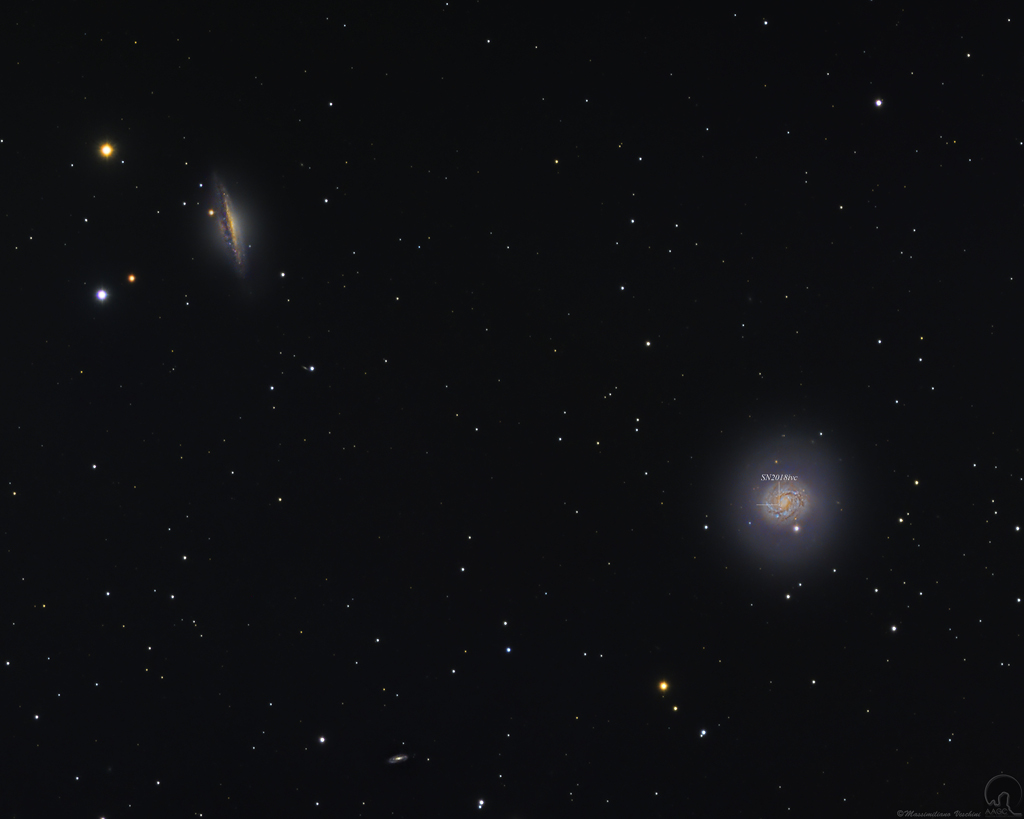
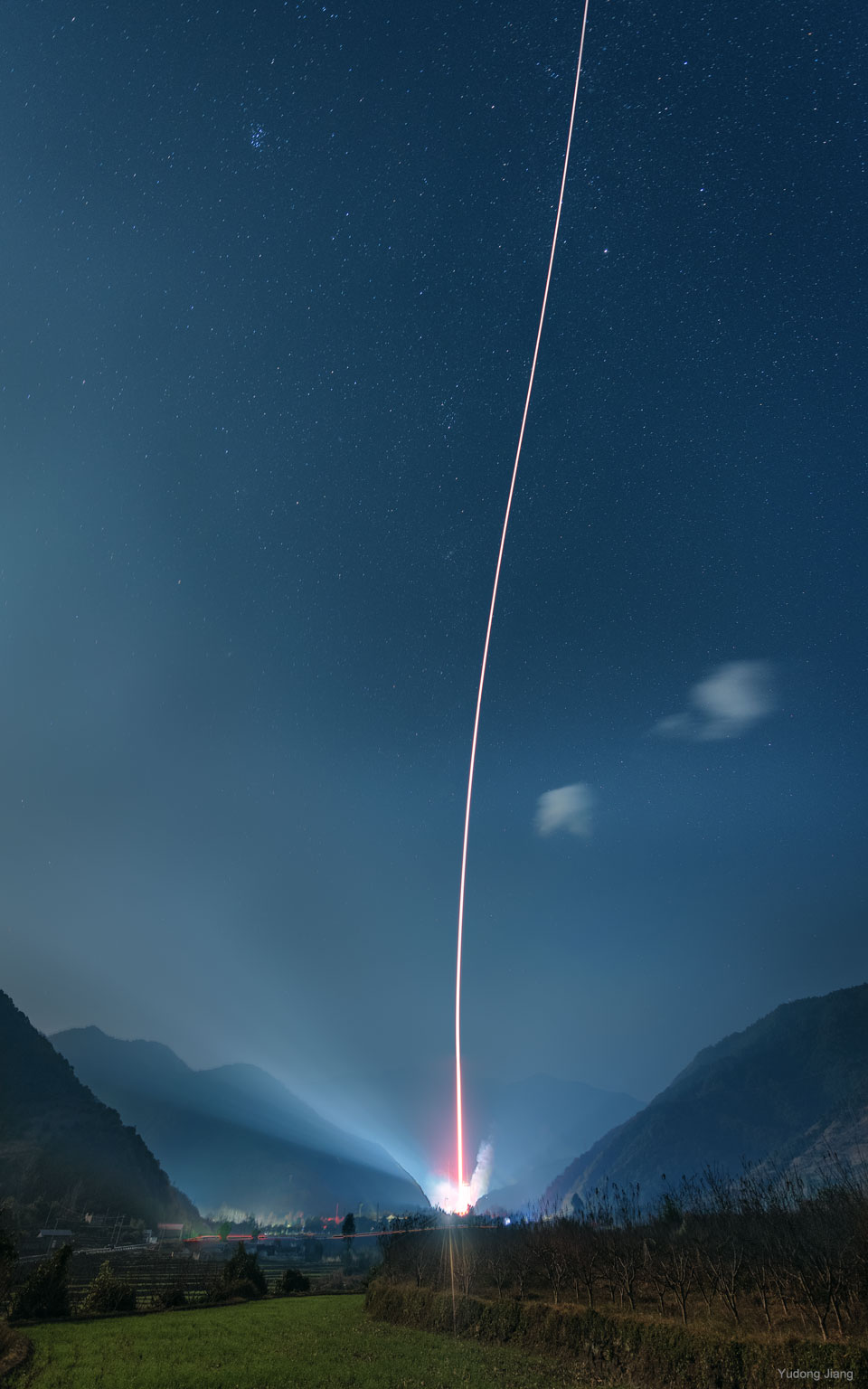
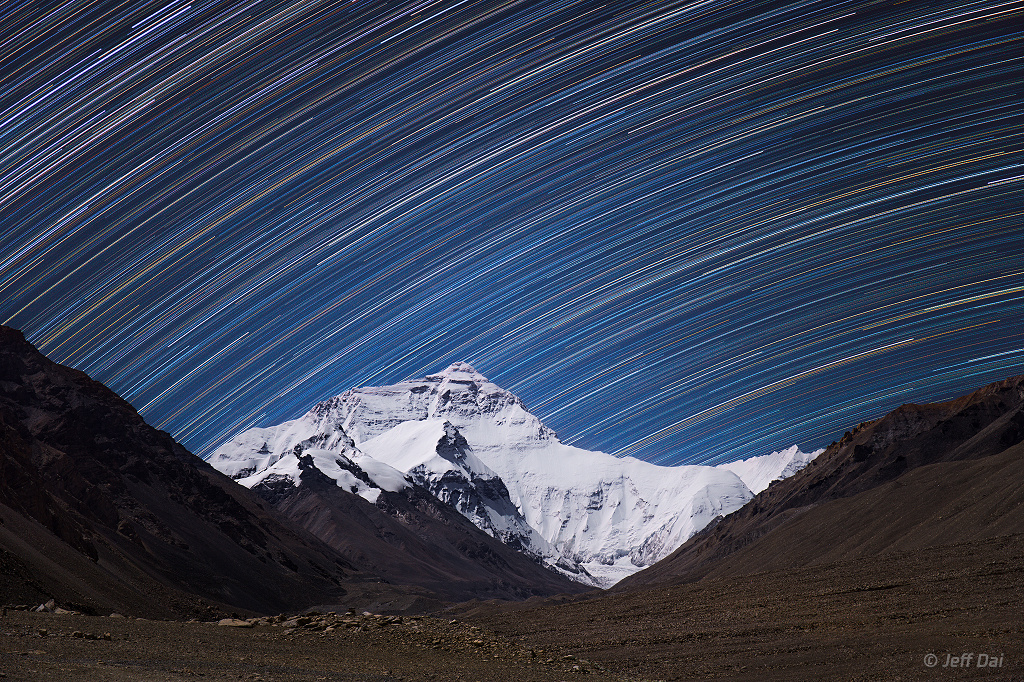
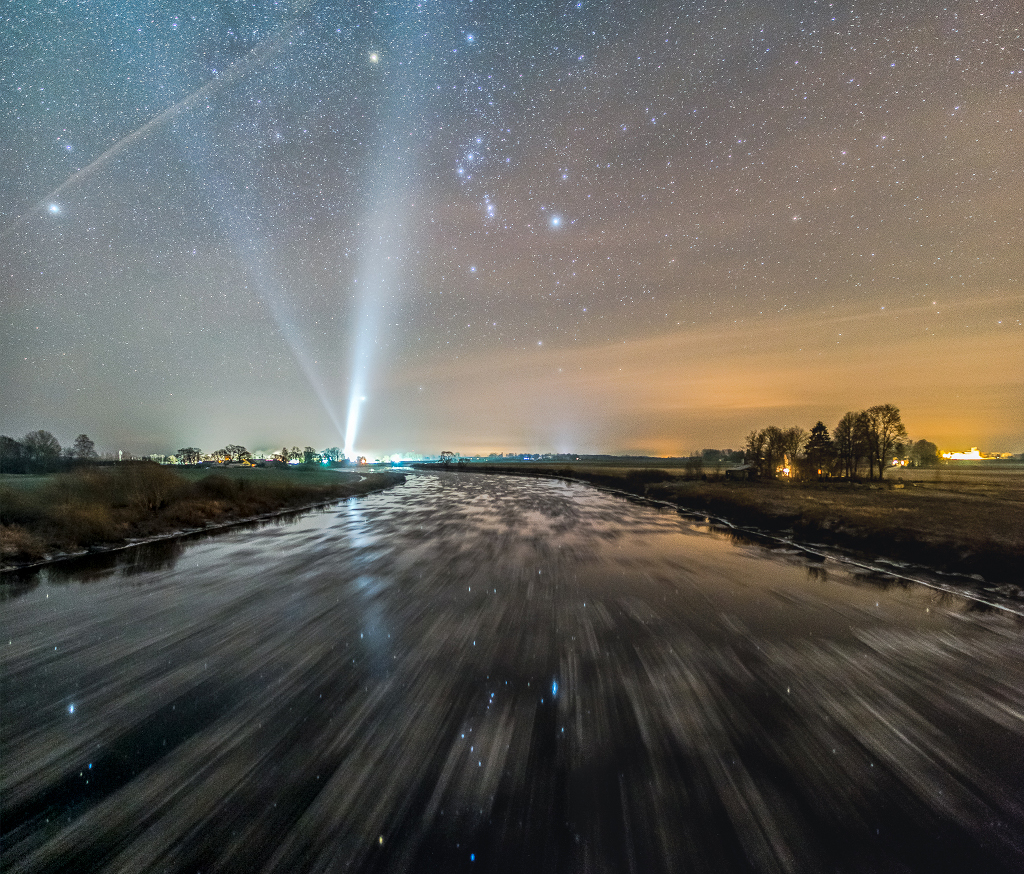
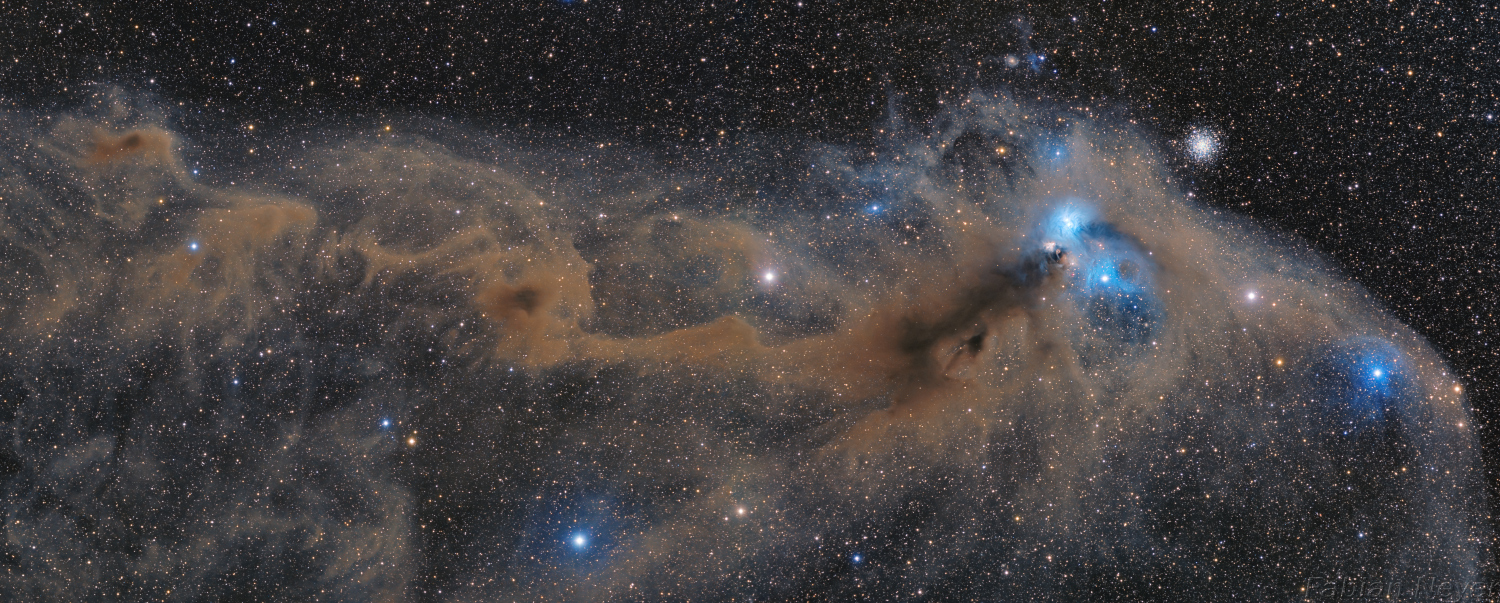
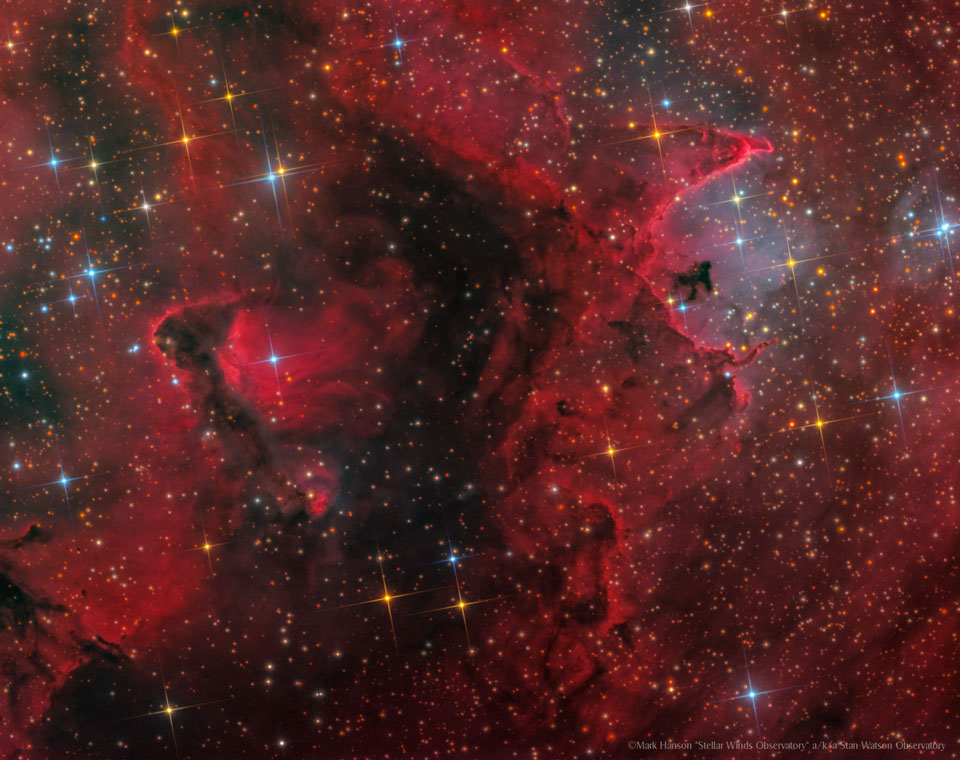
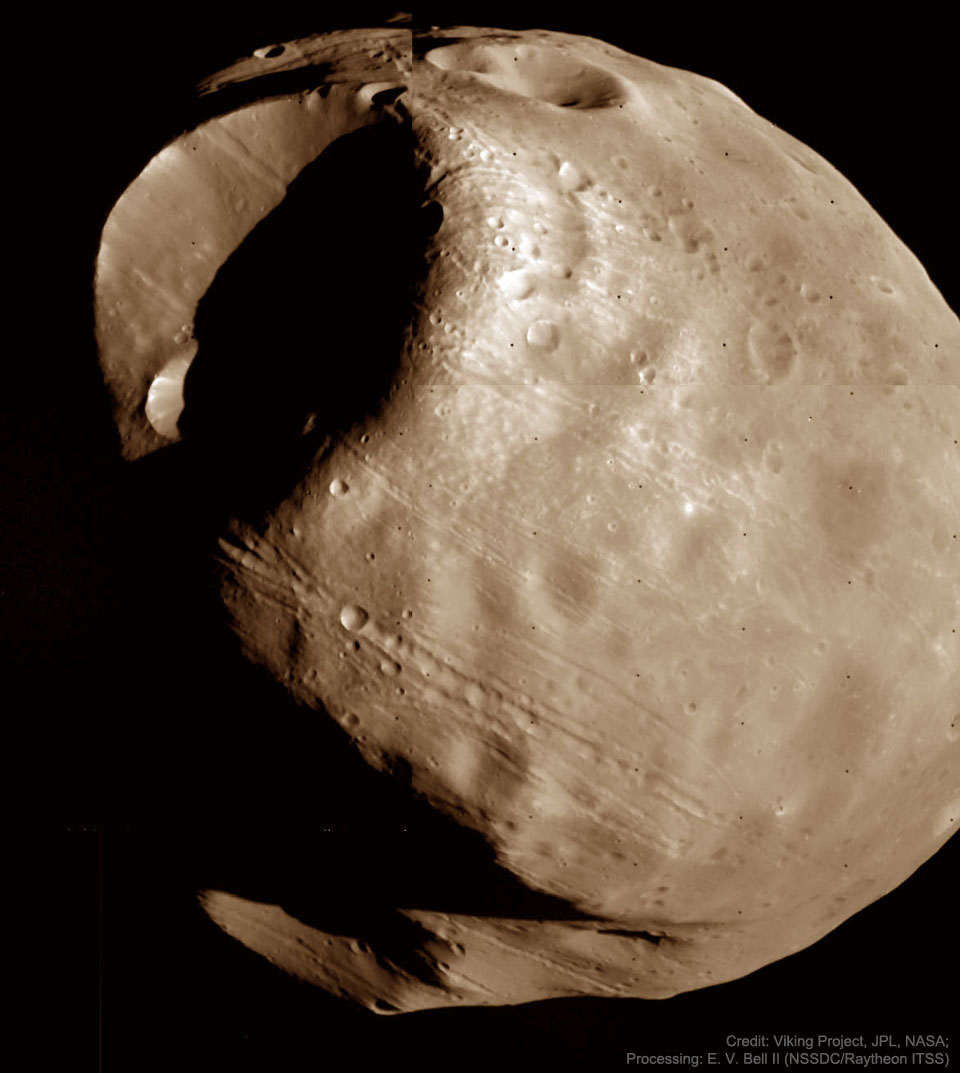
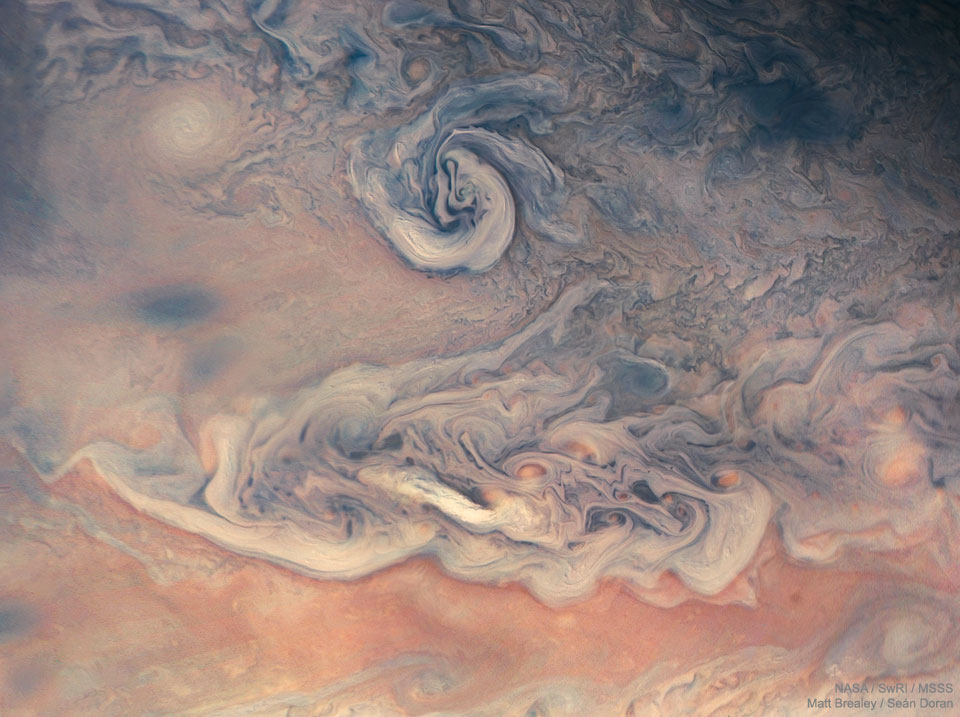
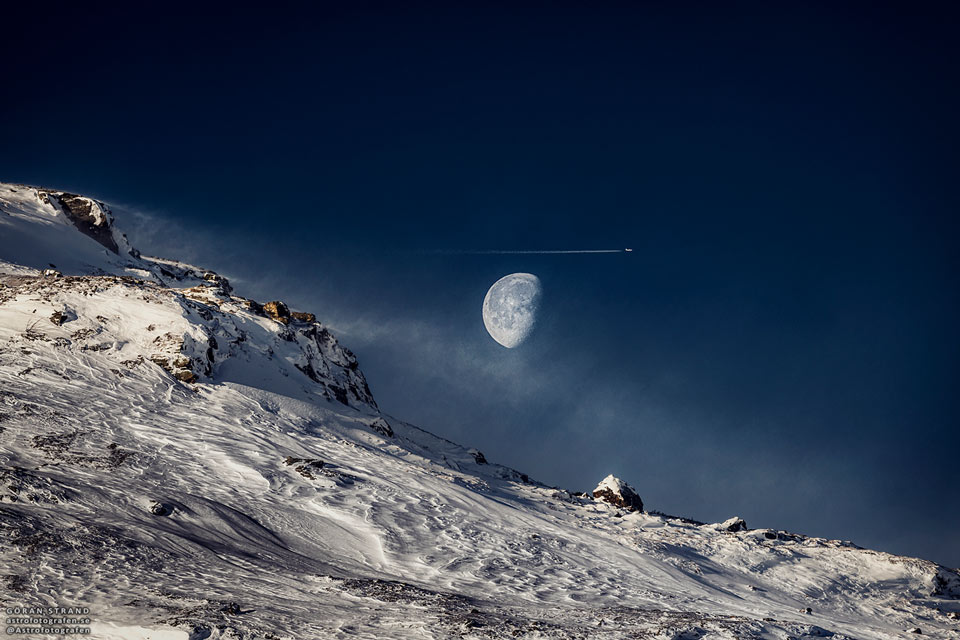
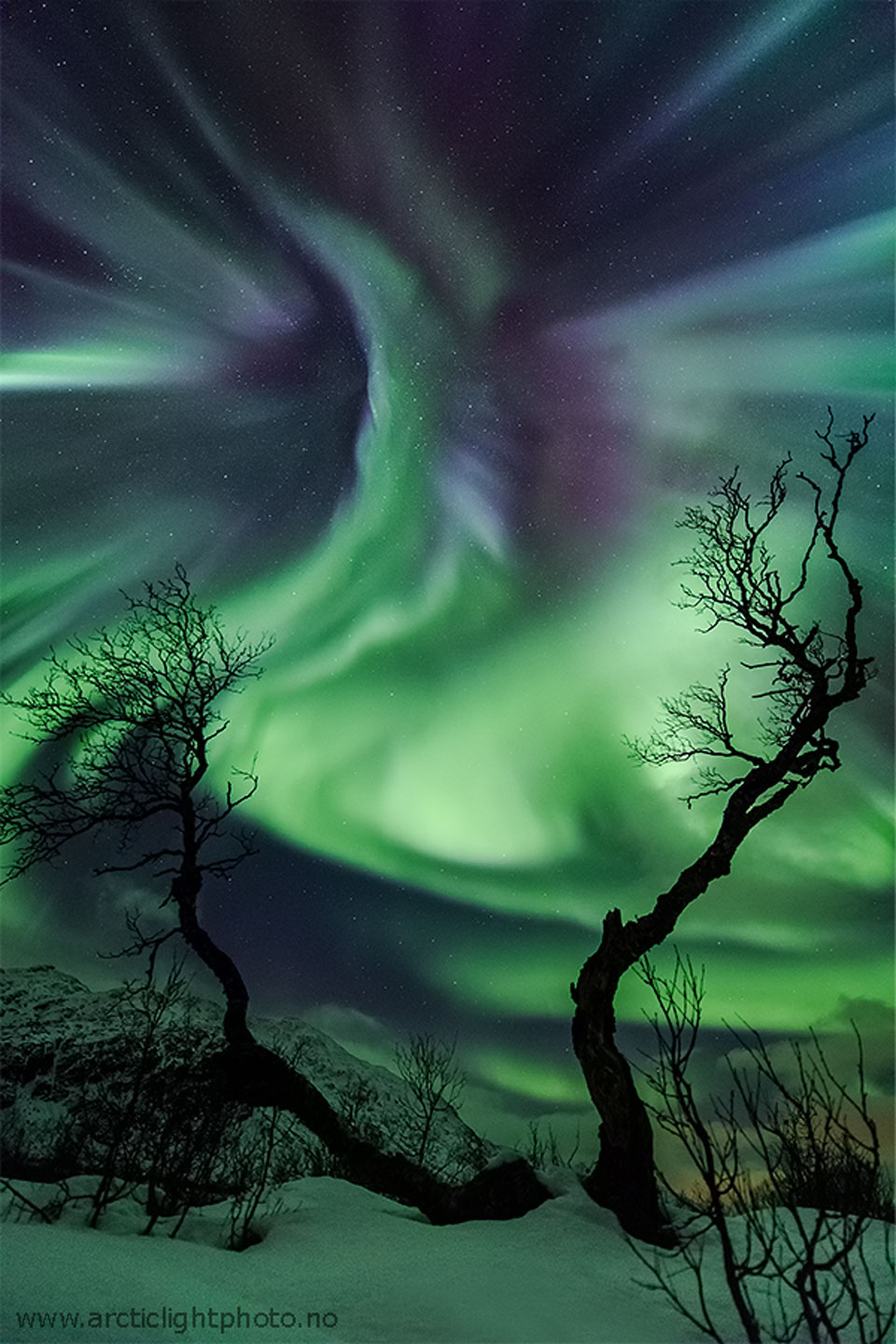
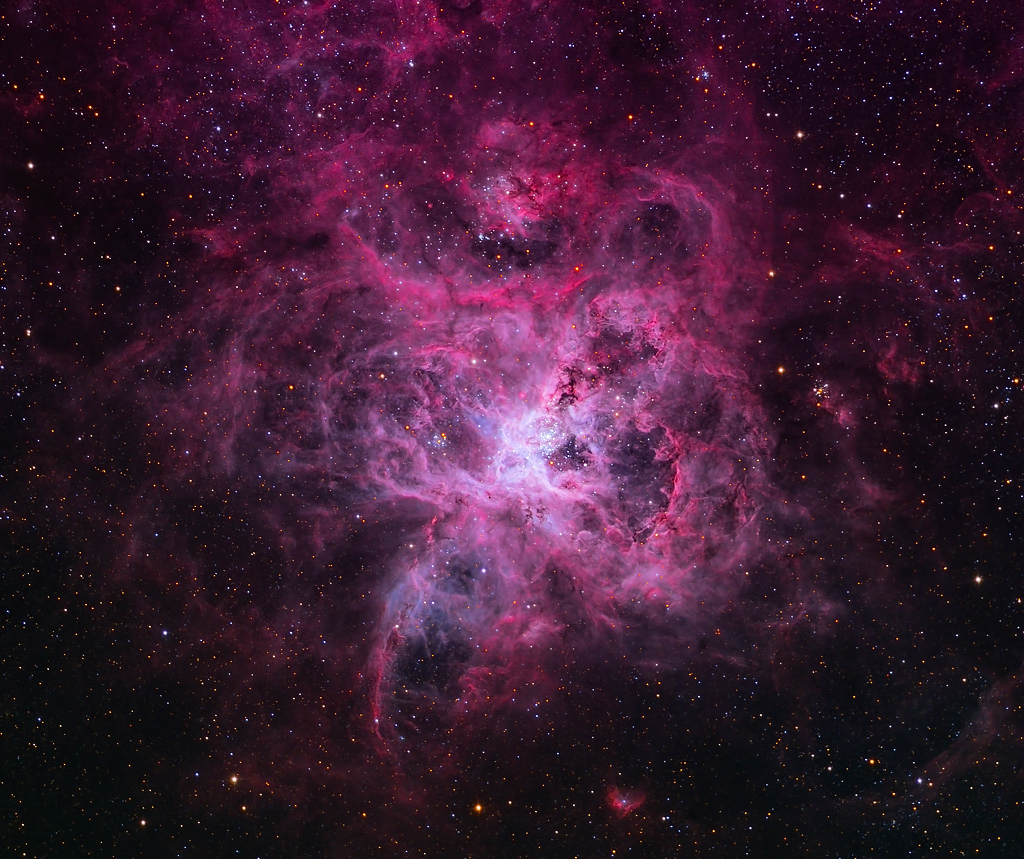
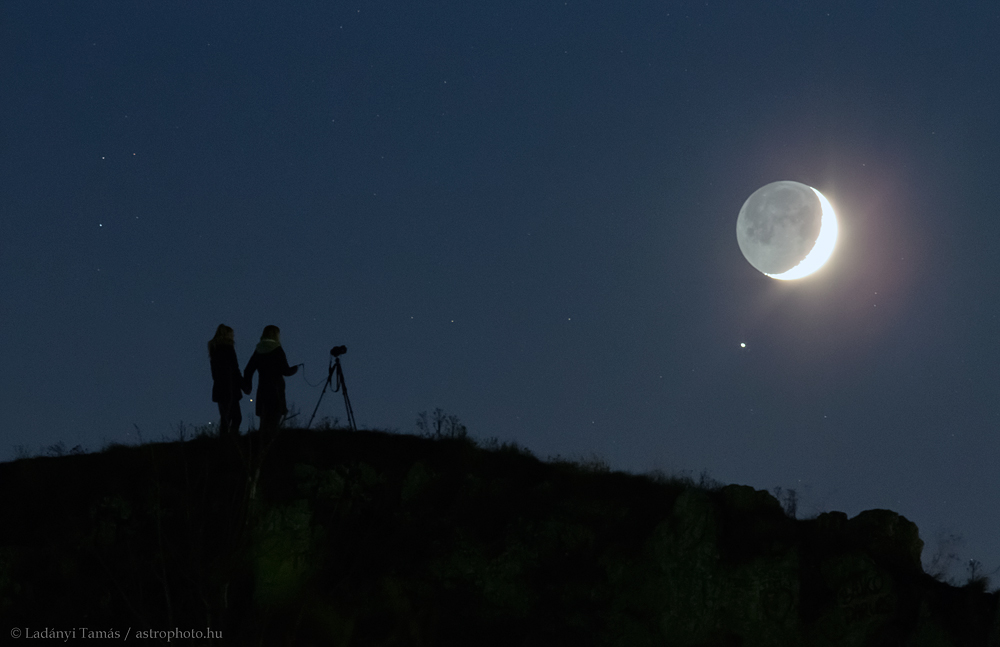
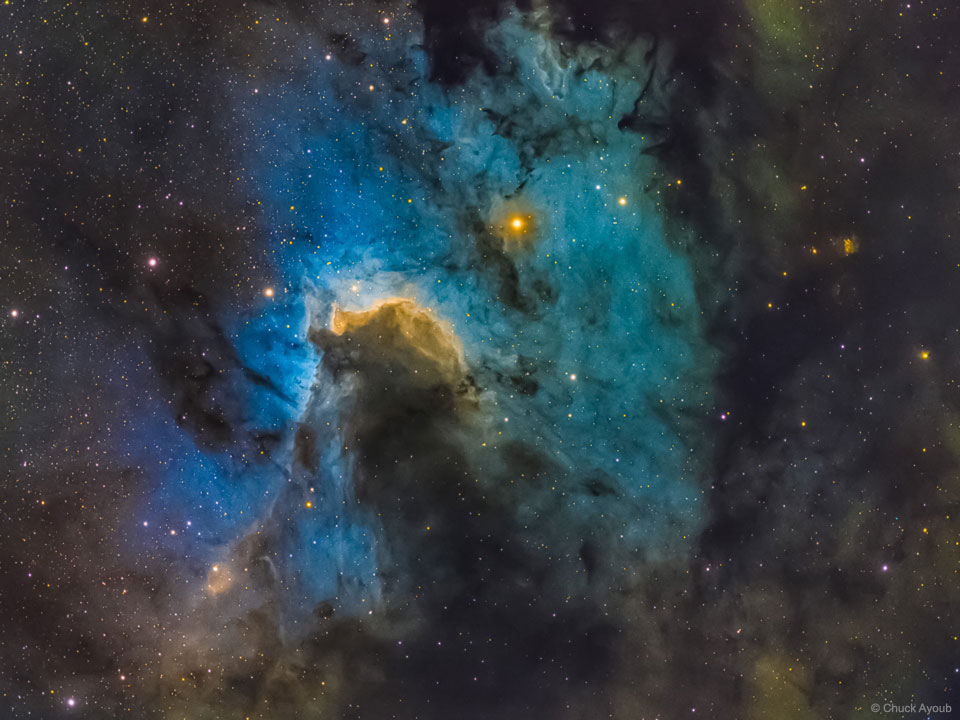
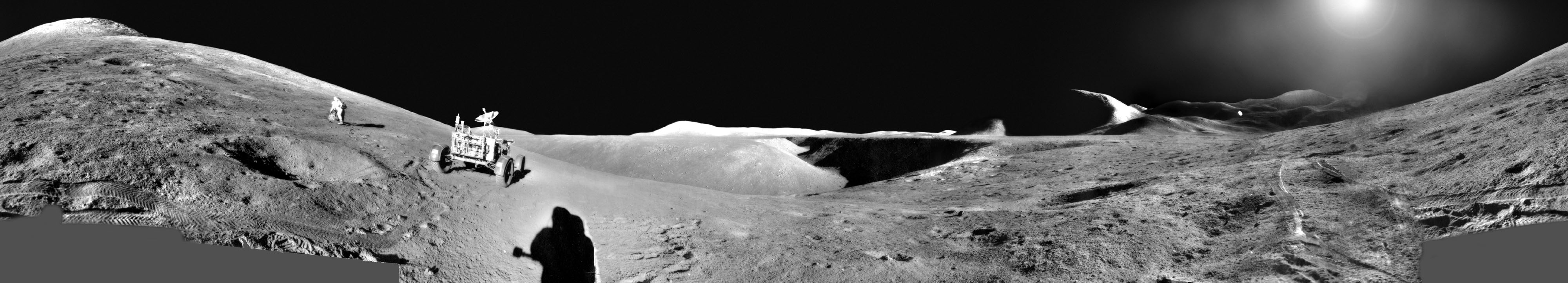
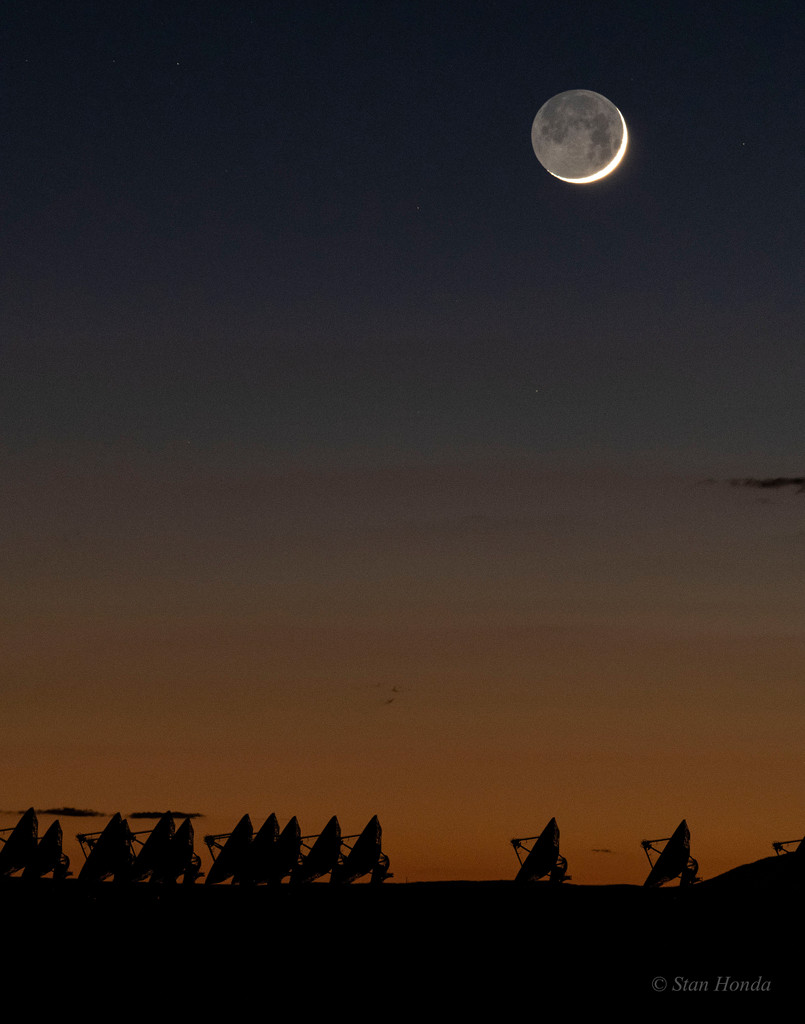
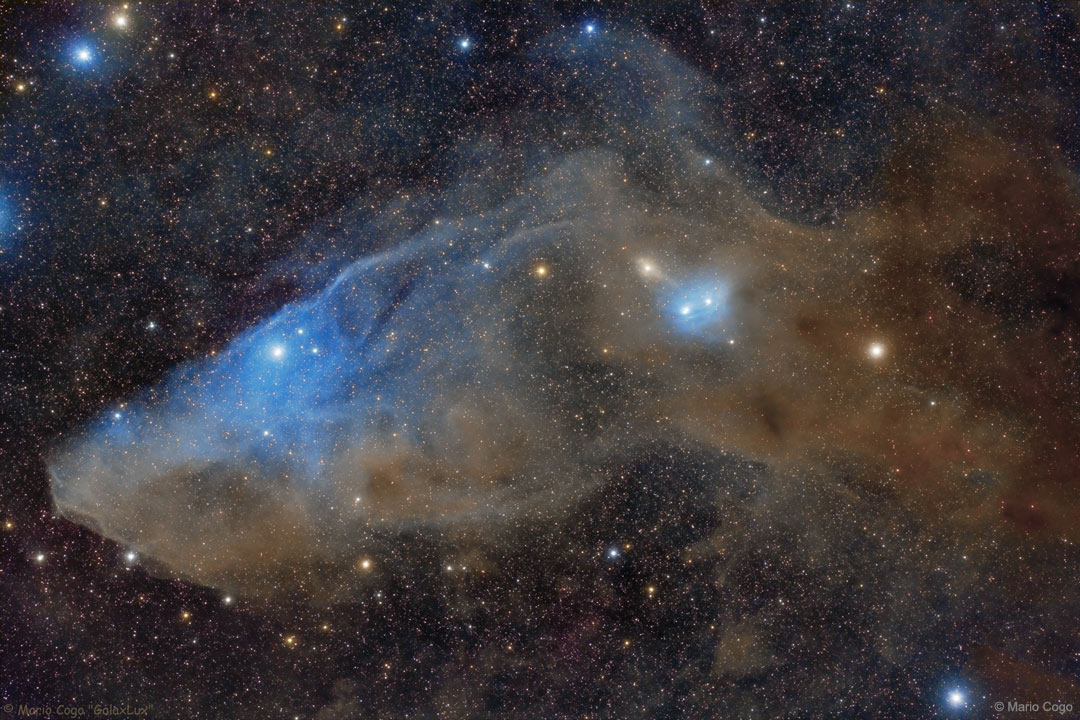
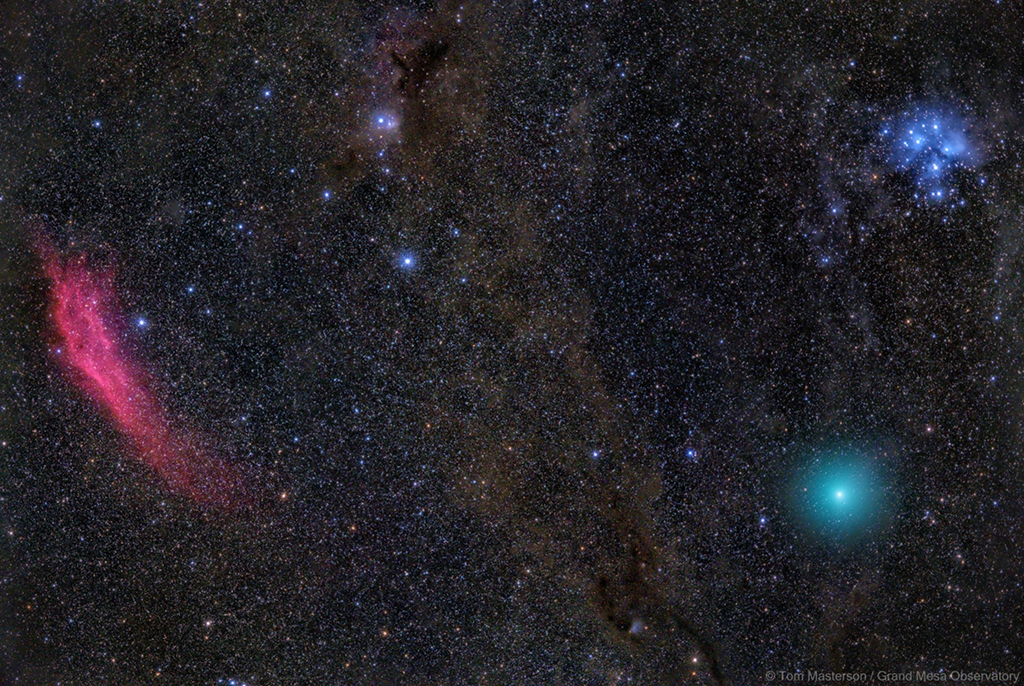
Double, double toil and trouble; Fire burn, and cauldron bubble .... maybe Macbeth should have consulted the Witch Head Nebula. A frighteningly shaped reflection nebula, this cosmic crone is about 800 light-years away though. Its malevolent visage seems to glare toward nearby bright star Rigel in Orion, just off the right edge of this frame. More formally known as IC 2118, the interstellar cloud of dust and gas is nearly 70 light-years across, its dust grains reflecting Rigel's starlight. In this composite portrait, the nebula's color is caused not only by the star's intense bluish light but because the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The same physical process causes Earth's daytime sky to appear blue, although the scatterers in planet Earth's atmosphere are molecules of nitrogen and oxygen. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2EYholA