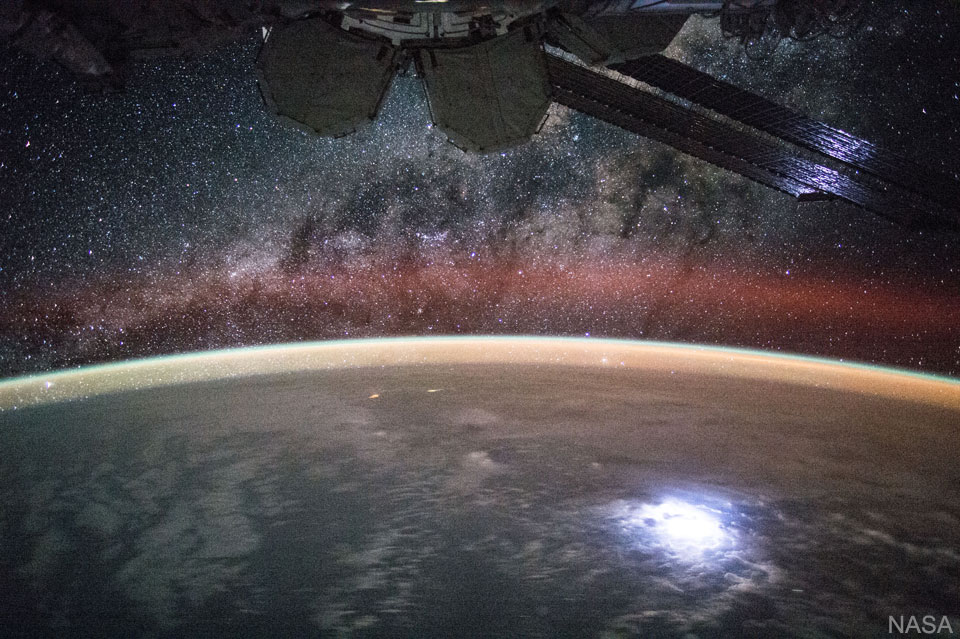
Why would the sky glow red? Aurora. A solar storm in 2012, emanating mostly from active sunspot region 1402, showered particles on the Earth that excited oxygen atoms high in the Earth's atmosphere. As the excited element's electrons fell back to their ground state, they emitted a red glow. Were oxygen atoms lower in Earth's atmosphere excited, the glow would be predominantly green. Pictured here, this high red aurora is visible just above the horizon last week near Flinders, Victoria, Australia. The sky that night, however, also glowed with more familiar but more distant objects, including the central disk of our Milky Way Galaxy on the left, and the neighboring Large and Small Magellanic Cloud galaxies on the right. A time-lapse video highlighting auroras visible that night puts the picturesque scene in context. Why the sky did not also glow green remains unknown. via NASA http://ift.tt/2js1m49